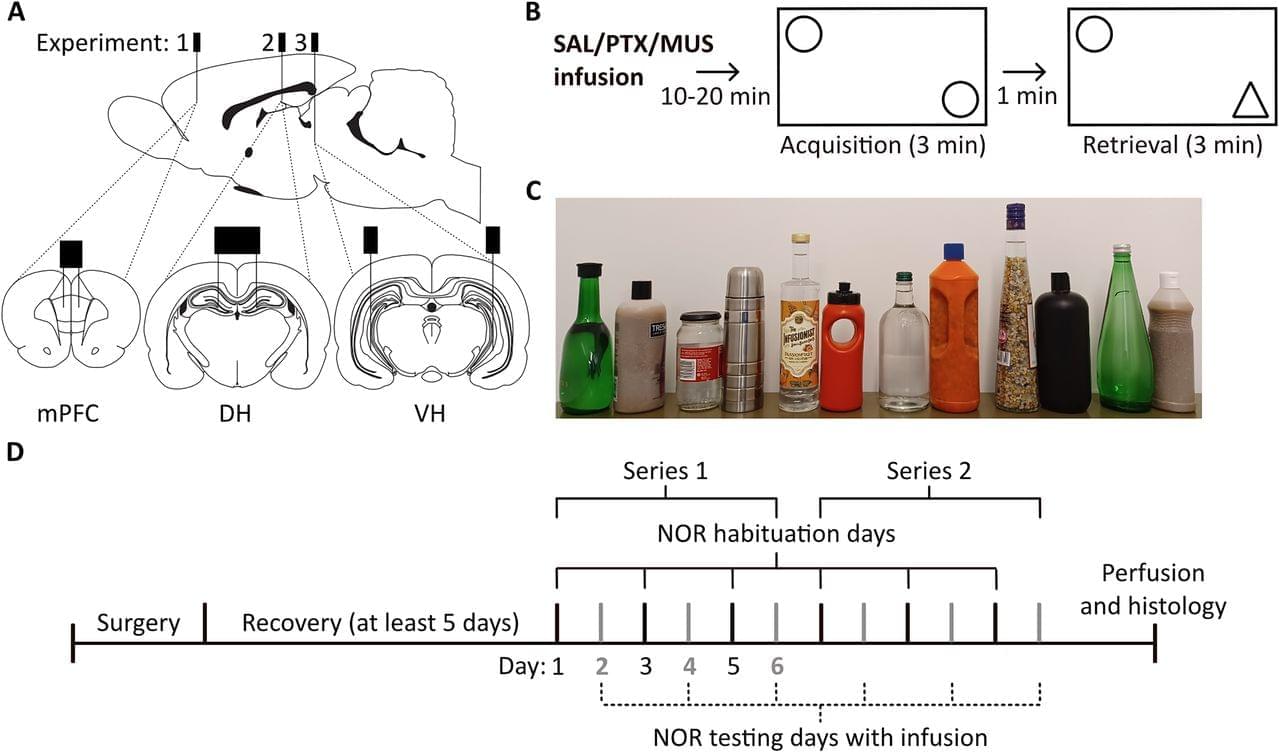
Impaired GABAergic inhibition, so-called neural disinhibition, in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus has been linked to cognitive deficits. The novel object recognition (NOR) task has been used widely to study cognitive deficits in rodents. However, the contribution of prefrontal cortical and hippocampal GABAergic inhibition to NOR task performance has not been established. Here, we investigated NOR task performance in male Lister hooded rats following regional neural disinhibition or functional inhibition, using intracerebral microinfusion of the GABAA receptor antagonist picrotoxin or agonist muscimol, respectively. Our infusion targets were the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), dorsal hippocampus (DH), and ventral hippocampus (VH).