As people age, these cells become defective and lose their ability to renew and repair the blood system, decreasing the body’s ability to fight infections as seen in older adults. Another example is a condition called clonal hematopoiesis; this asymptomatic condition is considered a premalignant state that increases the risk of developing blood cancers and other inflammatory disorders. Its prevalence increases significantly with age.
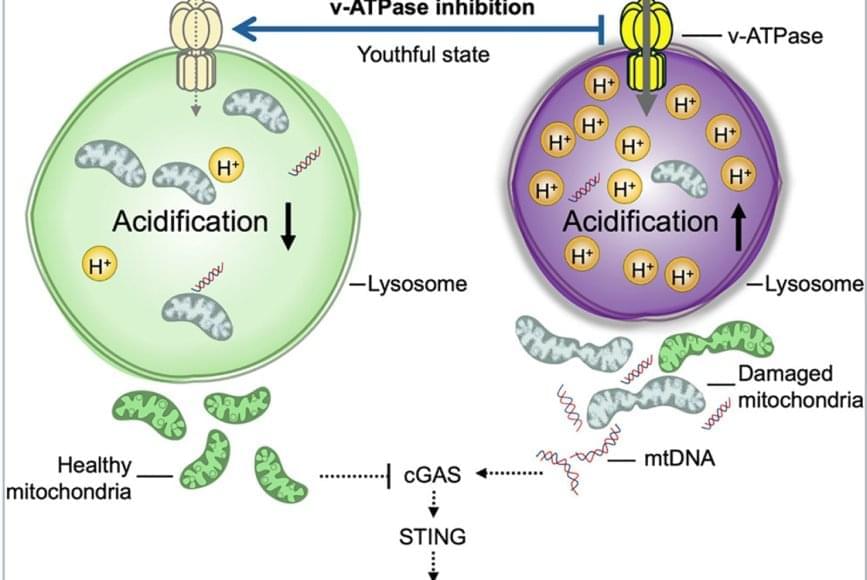
The team discovered that lysosomes in aged HSCs become hyper-acidic, depleted, damaged, and abnormally activated, disrupting the cells’ metabolic and epigenetic stability. Using single-cell transcriptomics and stringent functional assays, the researchers found that suppressing this hyperactivation with a specific vacuolar ATPase inhibitor restored lysosomal integrity and blood-forming stem cell function.
The old stem cells started acting young and healthy once more. Old stem cells regained their regenerative potential and ability to be transplanted and to produce more healthy stem cells and blood that is balanced in immune cells; they renewed their metabolism and mitochondrial function, improved their epigenome, reduced their inflammation, and stopped sending out “inflammation” signals that can cause damage in the body.
Remarkably, ex vivo treatment (when cells are removed from the body, modified in a laboratory, and returned to the body) of old stem cells with the lysosomal inhibitor boosted their in vivo blood-forming capacity more than eightfold, demonstrating that correcting lysosomal dysfunction can restore regenerative potential.
This restoration also dampened harmful inflammatory and interferon-driven pathways by improving lysosomal processing of mitochondrial DNA and reducing activation of the cGAS-STING immune signaling pathway, which they find to be a key driver of inflammation and aging of stem cells.
Researchers have discovered how to reverse aging in blood-forming stem cells in mice by correcting defects in the stem cell’s lysosomes. The breakthrough, published in Cell Stem Cell, identifies lysosomal hyperactivation and dysfunction as key drivers of stem cell aging and shows that restoring lysosomal slow degradation can revitalize aged stem cells and enhance their regenerative capacity.
Lysosomes are specialized structures that act as the cell’s recycling system, breaking down proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Lysosomes accumulate and degrade waste, and eventually recycle it to be reused in biosynthetic processes. Lysosomes can also store nutrients to be released when needed. Lysosomes are recognized as pivotal for regulating metabolism in the cell, both catabolism (breaking down complex molecules to simple ones) and anabolism (building complex molecules from simpler ones).
The study focuses on hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). These are the rare long-lived cells in the bone marrow responsible for generating all blood and immune cells.