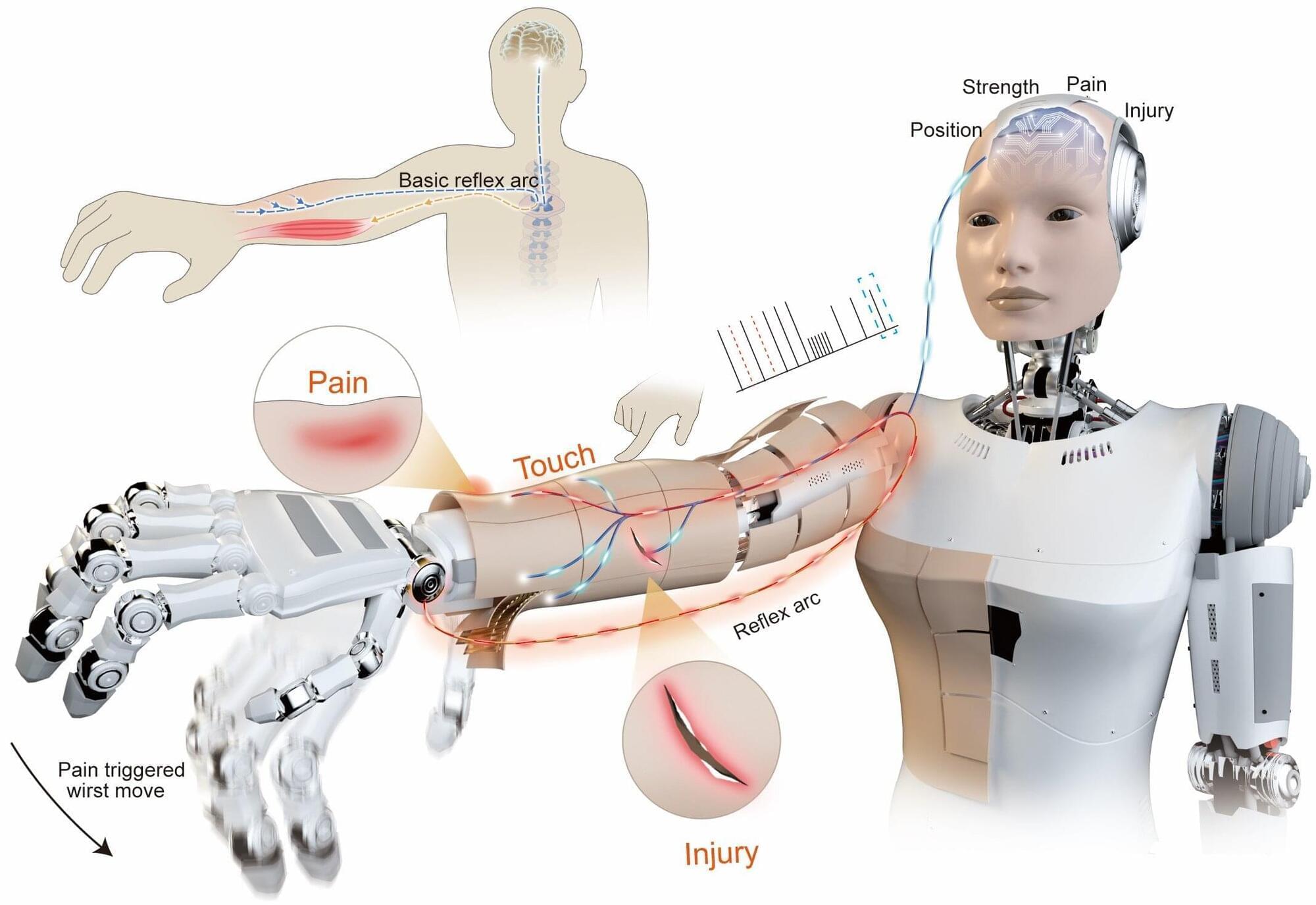
If you accidentally put your hand on a hot object, you’ll naturally pull it away fast, before you have to think about it. This happens thanks to sensory nerves in your skin that send a lightning-fast signal to your spinal cord, which immediately activates your muscles. The speed at which this happens helps prevent serious burns. Your brain is only informed once the movement has already started.
If something similar happens to a humanoid robot, it typically has to send sensor data to a central processing unit (CPU), wait for the system to process it, and then send a command to the arm’s actuators to move. Even a brief delay can increase the risk of serious damage.
But as humanoid robots move out of labs and factories and into our homes, hospitals and workplaces, they will need to be more than just pre-programmed machines if they are to live up to their potential. Ideally, they should be able to interact with the environment instinctively. To help make that happen, scientists in China have developed a neuromorphic robotic e-skin (NRE-skin) that gives robots a sense of touch and even an ability to feel pain.