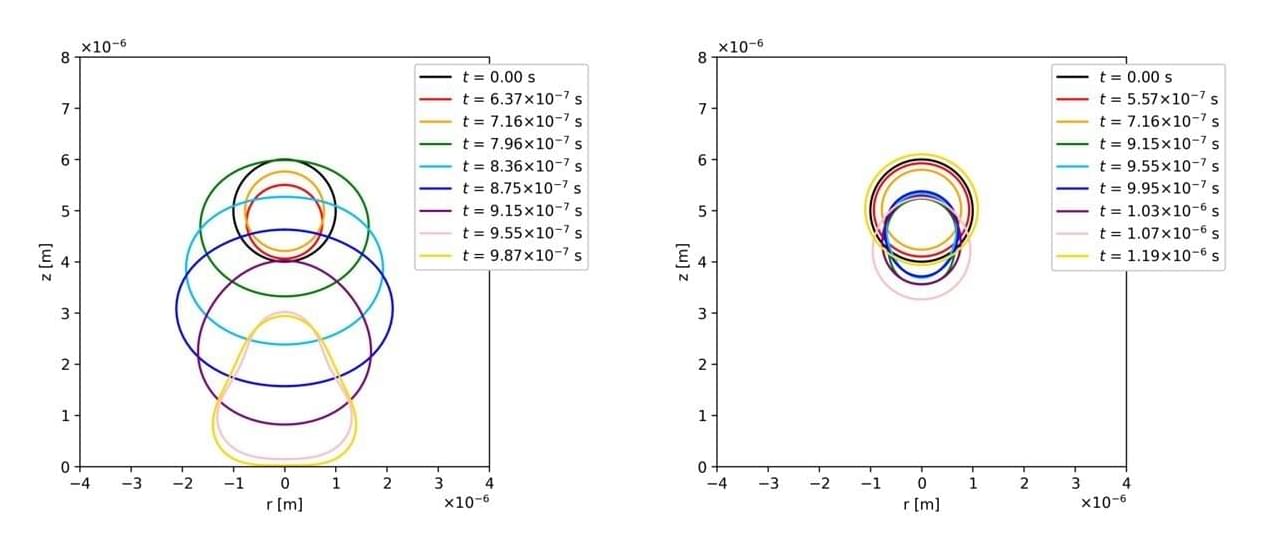
Encapsulated microbubbles (EMBs), tiny gas-filled bubbles coated in lipid or protein shells, play a central role in biomedical ultrasound. When exposed to ultrasound waves, EMBs contract, resulting in oscillations that enhance image contrast or deliver drugs directly by creating pores in cell membranes via sonoporation. However, while promising for biomedical applications, their behavior is far more complex.
Most existing theories on EMBs assume spherically symmetrical oscillations and only study them in simple Newtonian fluids. However, most biological fluids, such as blood, are viscoelastic (non-Newtonian) fluids. When inside the body, these fluid forces, pressure from vessel walls, and changing ultrasound pulses can influence the behavior of EMBs, affecting both imaging accuracy and treatment safety.
To better understand these effects, a multi-institutional research team has developed a comprehensive computational model that simulates the behavior of EMBs under real biological conditions. The team included Assistant Professor Haruki Furukawa and Professor Shuichi Iwata from Nagoya Institute of Technology (NITech), Japan, in collaboration with Emeritus Professor Tim N. Phillips, Dr. Michael J. Walters, and Reader Steven J. Lind from Cardiff University, Wales.