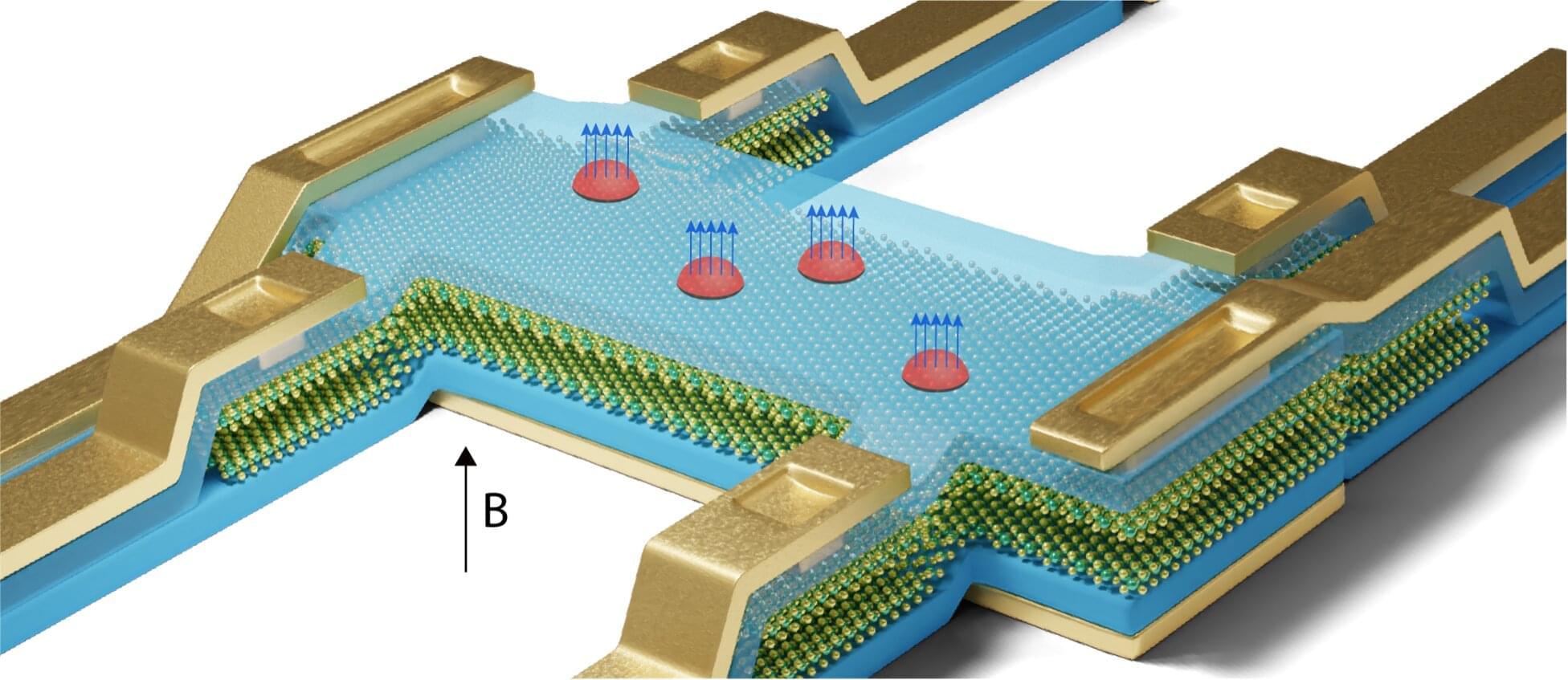
Semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are a class of layered materials exhibiting unique optoelectronic properties that could be leveraged to develop transistors, sensors and other nanoelectronics. Despite their advantages, creating robust ohmic contacts that connect a metal electrode in transistors to semiconducting TMDs at cryogenic temperatures has proved challenging.
This has so far limited the use of these materials for either studying fundamental physics or developing nanoelectronics that operate at low temperatures.
In a paper in Nature Electronics, researchers at the Liaoning Academy of Materials, Shanxi University and other institutes introduced a new technique for realizing ohmic contacts to the TMD molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) at cryogenic temperatures, and found that electron mobility in those transistors can be surprisingly high.