This study externally validated the EHR-CAT risk score for cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) using the Epic Cosmos database, with similar performance as the original derivation, showing promise EHR integration across diverse health systems.
Question Can routinely collected electronic health record (EHR) data from diverse health systems be used to model cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) risk?
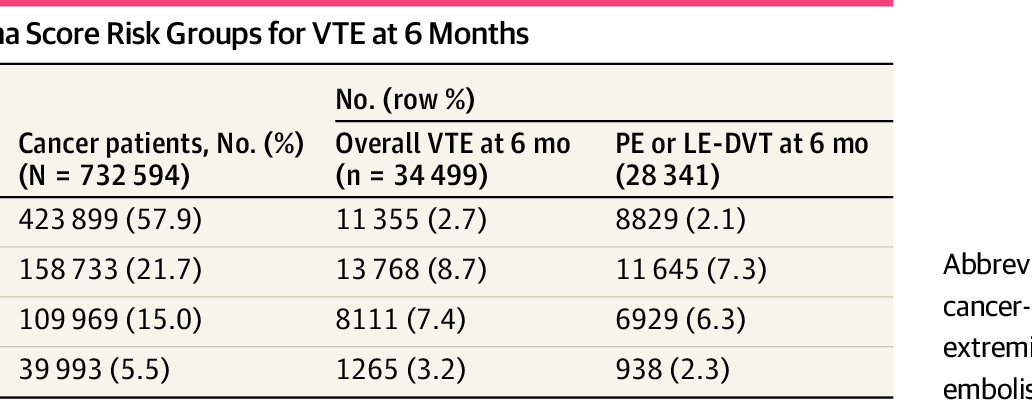
Findings In this prognostic study using a retrospective cohort of 732 594 patients with cancer receiving systemic therapy between 2018 and 2023 from 184 health systems, the EHR-CAT score significantly outperformed the benchmark Khorana score and had 20% improved accuracy. The model had consistent calibration by demographic subgroups, health system sites, and cohorts stratified by bleeding risk.
Meaning These results suggest that standardized structured EHR data from different health systems can support scalable validation and implementation of CAT risk assessment.