The accompanying diagram presents a comprehensive anatomical overview of the human brain, integrating both lateral surface morphology and a midsagittal section to illustrate the spatial organization of cortical and subcortical structures. Major gyri, sulci, and lobar divisions are delineated alongside deep nuclei, commissural pathways, and the ventricular system. The transparent rendering of the ventricles highlights their relationship to surrounding neural tissue and emphasizes the topology of cerebrospinal fluid pathways. This visualization serves as a structural reference point for understanding functional domains such as sensorimotor processing, higher-order cognition, limbic integration, and autonomic regulation. Collectively, the diagram provides a detailed framework for interpreting neuroanatomical connectivity and its relevance to neural function.
#study:
Cerebrospinal Fluid Mechanics and Its Coupling to Cerebrovascular Dynamics: https://www.annualreviews.org/content/journals/10.1146/annur…#45;034321
CSF dynamics throughout the ventricular system using 4D flow MRI: associations to arterial pulsatility, ventricular volumes, and age: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12987-024-00570-4
Fundamental functional differences between gyri and sulci: implications for brain function, cognition, and behavior: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38665307/?utm_source=chatgpt.com.
Brain ventricles as windows into brain development and disease: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S089662732…hatgpt.com
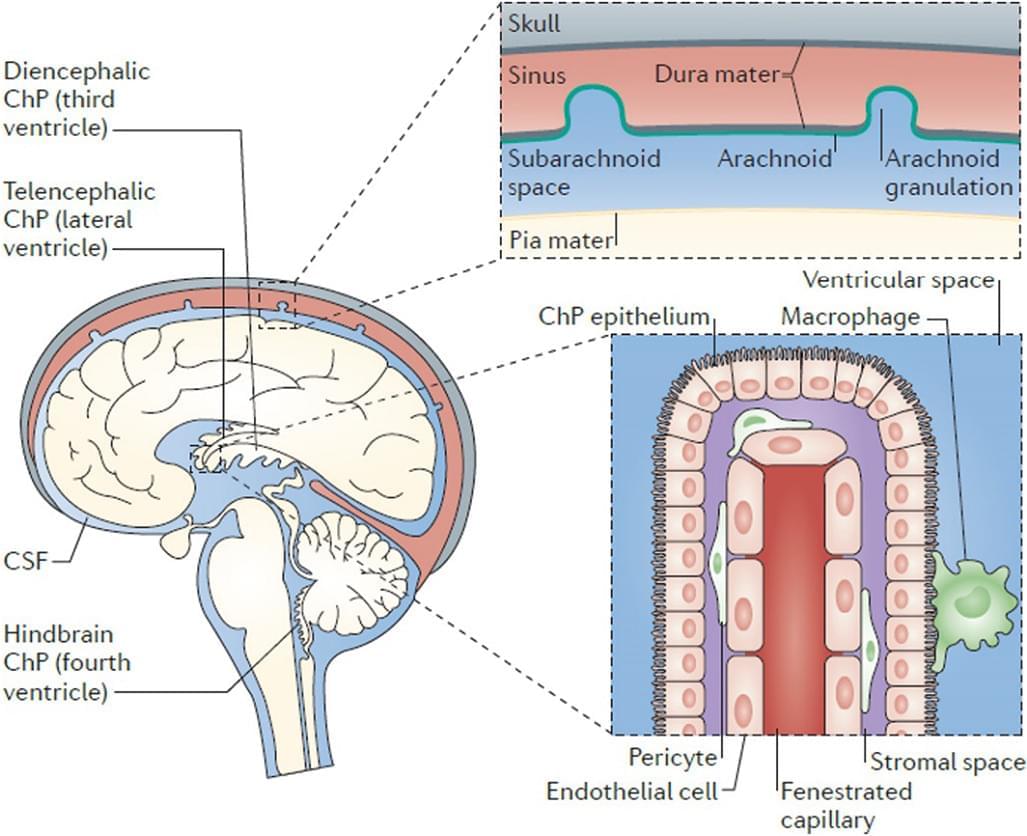
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), predominantly produced in the ventricles and circulating throughout the brain and spinal cord, is a key protective mechanism of the central nervous system (CNS). Physical cushioning, nutrient delivery, metabolic waste, including protein clearance, are key functions of the CSF in humans. CSF volume and flow dynamics regulate intracranial pressure and are fundamental to diagnosing disorders including normal pressure hydrocephalus, intracranial hypotension, CSF leaks, and possibly Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The ability of CSF to clear normal and pathological proteins, such as amyloid-beta (Aβ), tau, alpha synuclein and others, implicates it production, circulation, and composition, in many neuropathologies. Several neuroimaging modalities have been developed to probe CSF fluid dynamics and better relate CSF volume and flow to anatomy and clinical conditions.