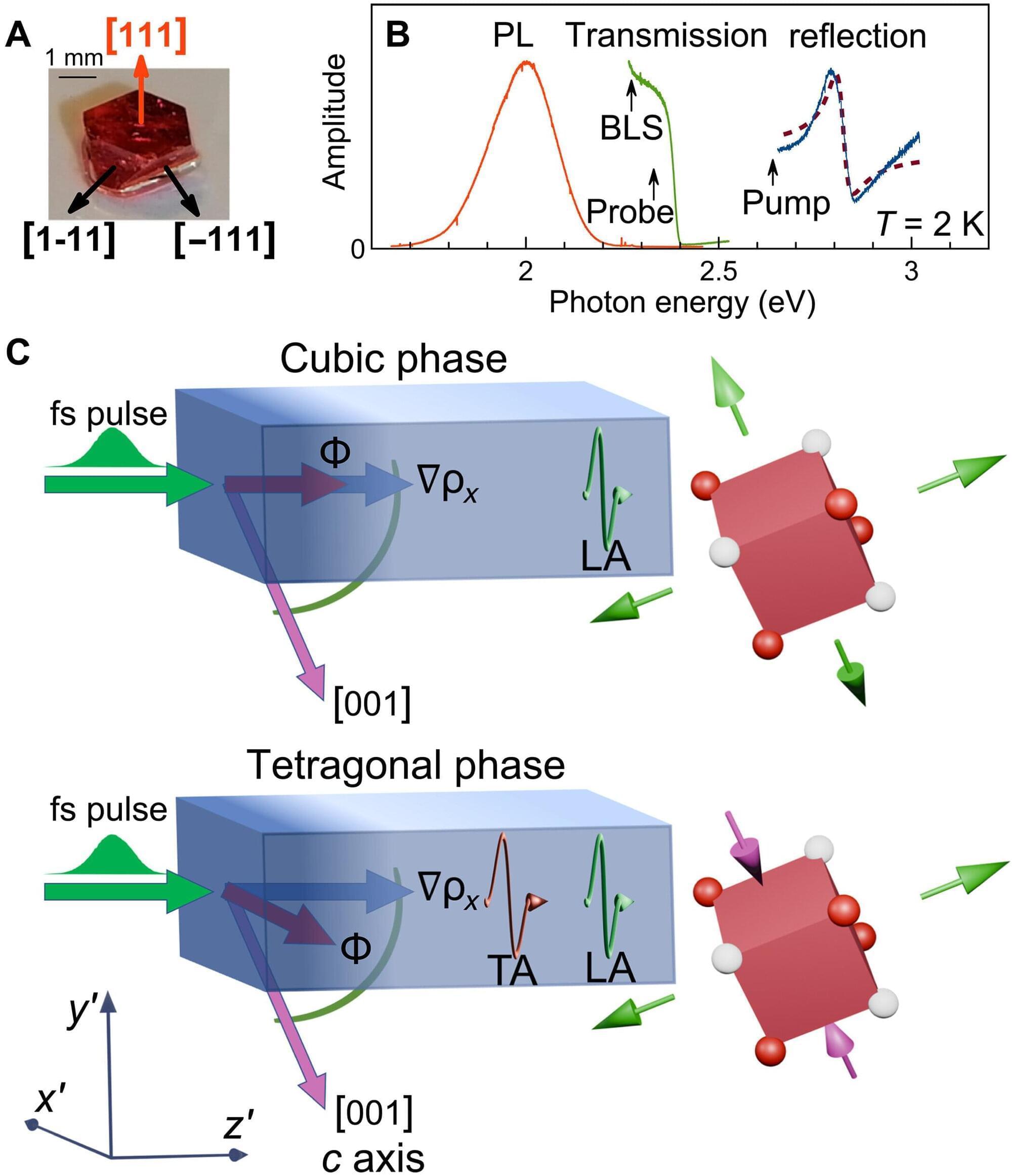
A German-French team of physicists from TU Dortmund University, University of Würzburg, and Le Mans Université has succeeded in launching shear hypersound pulses with exceptionally large amplitudes in metal halide perovskites using pulsed optical excitation.
This discovery is published in the journal Science Advances.
Whereas the material has been of high interest for photovoltaics so far, the new results turn it into a candidate to be used for optically driven devices capable of generating and detecting sound waves at sub-terahertz frequencies, with potential applications across electronic, photonic, magnetic, and biomedical devices.