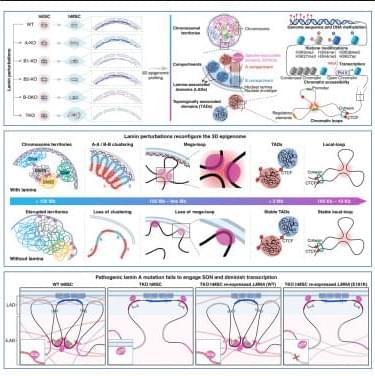
Wang et al. systematically depicted the lamins-guided 3D epigenome in human stem cells and demonstrated that lamins not only serve as key regulators of chromatin-NL tethering and large-scale genome organization but also are essential for the spatial positioning and clustering of nuclear speckle through direct interactions within the nuclear interior.