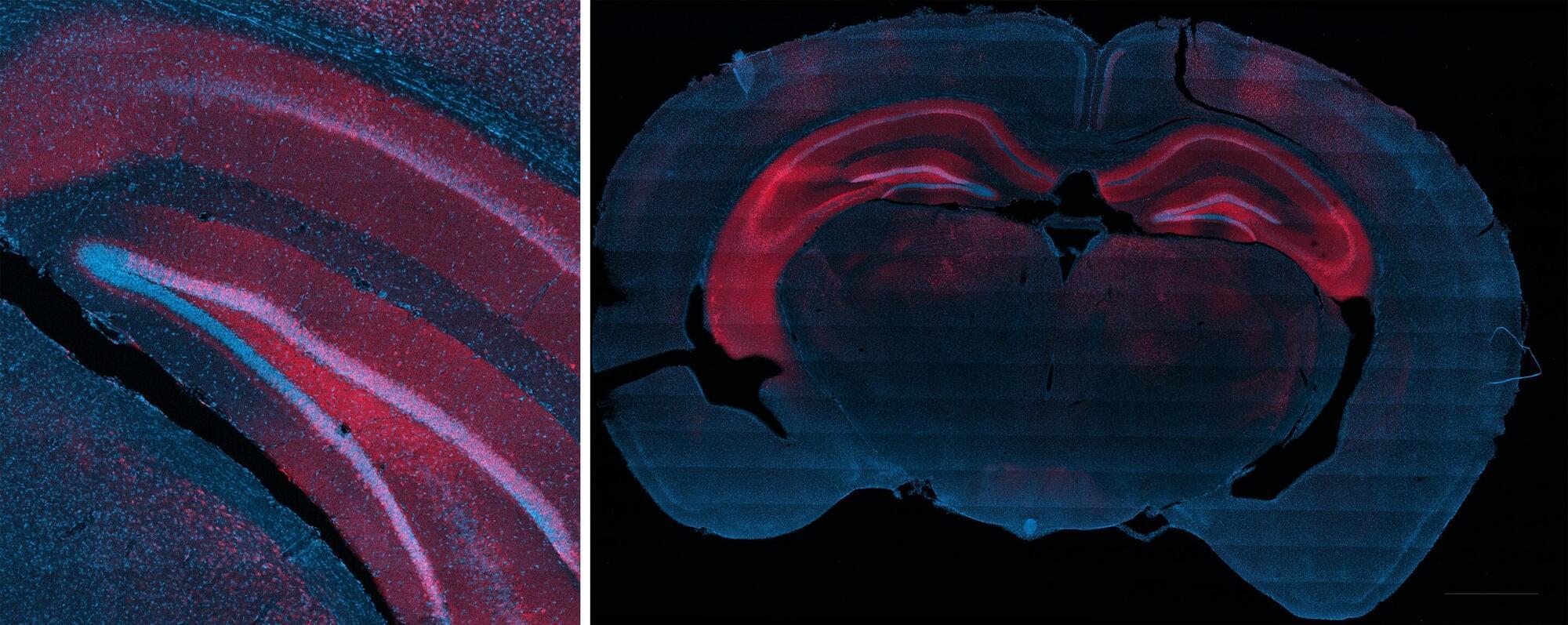
Rice University bioengineers have demonstrated a nonsurgical way to quiet a seizure-relevant brain circuit in an animal model. The team used low-intensity focused ultrasound to briefly open the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the hippocampus, delivered an engineered gene therapy only to that region and later flipped an on-demand “dimmer switch” with an oral drug.
The research shows that a one-time, targeted procedure can modulate a specific brain region without impacting off-target areas of the brain. It is published in and featured on the cover of ACS Chemical Neuroscience.
“Many neurological diseases are driven by hyperactive cells at a particular location in the brain,” said study lead Jerzy Szablowski, assistant professor of bioengineering and a member of the Rice Neuroengineering Initiative. “Our approach aims the therapy where it is needed and lets you control it when you need it, without surgery and without a permanent implant.”