In spaces smaller than a wavelength of light, electric currents jump from point to point and magnetic fields corkscrew through atomic lattices in ways that defy intuition. Scientists have only ever dreamed of observing these marvels directly.
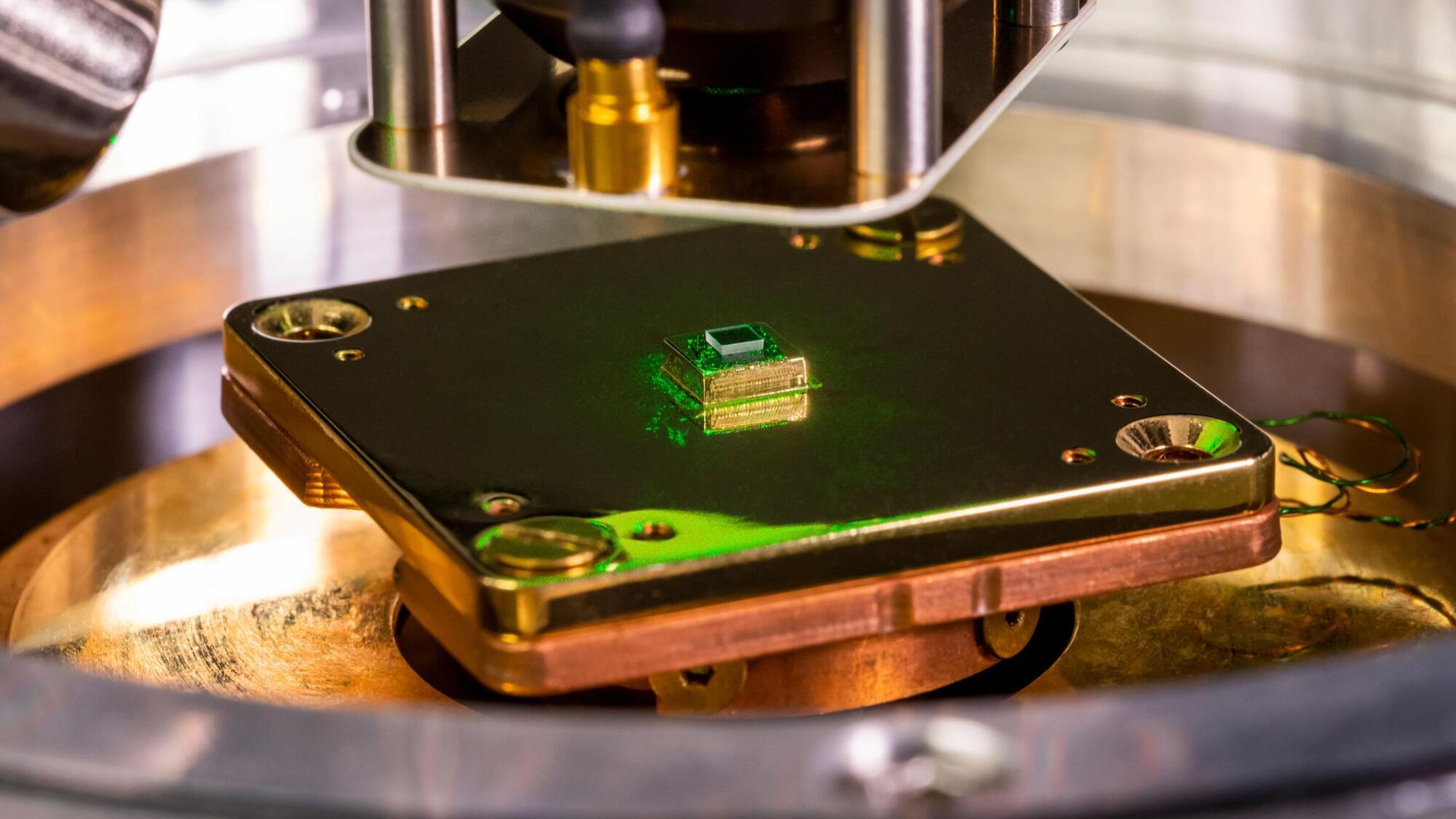
Now Princeton researchers have developed a diamond-based quantum sensor that reveals rich new information about magnetic phenomena at this minute scale. The technique uncovers fluctuations that are beyond the reach of existing instruments and provides key insight into materials such as graphene and superconductors. Superconductors have enabled today’s most advanced medical imaging tools and form the basis of hoped-for technologies like lossless powerlines and levitating trains.
The underlying diamond-based sensing methods have been under development for half a decade. But in a Nov. 27 paper in Nature, the team reported roughly 40 times greater sensitivity than previous techniques.