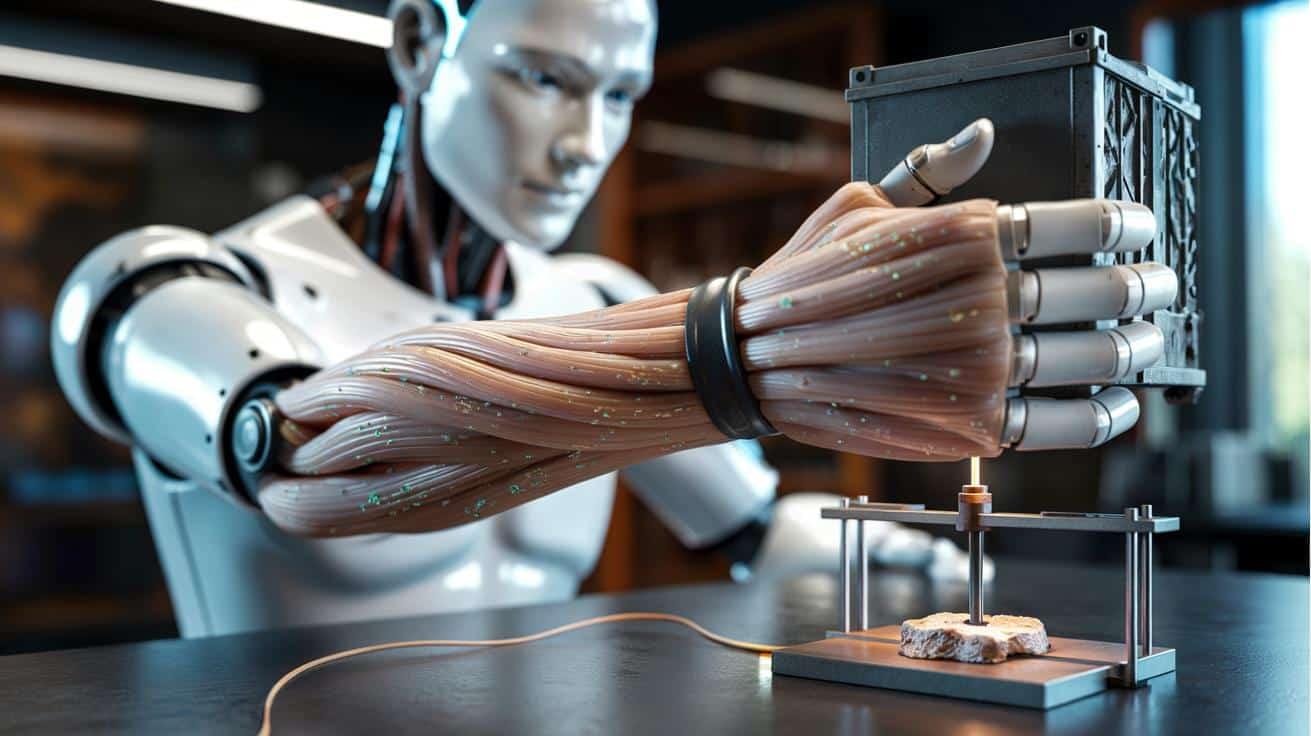
A new material bends that rule.
Researchers in South Korea say they have built a soft, magnetic artificial muscle that hits hard numbers without turning into a stiff piston. The material flexes, contracts and relaxes like flesh, yet ramps up stiffness on demand when asked to do real work. That mix has long sat out of reach for humanoid robots that need both agility and strength.
Most humanoids move with a cocktail of motors, gears and pneumatic lines. These systems deliver power, but they also add bulk and make contact risky. Soft actuators change the equation. They integrate into limbs, cushion impacts and tolerate misalignment. They also weigh far less than hydraulic stacks and slot neatly inside compact forms like hands, faces and torsos.