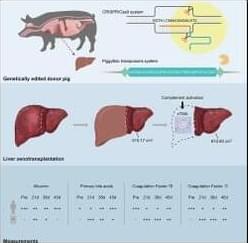
The advent of genetically edited porcine-to-human xenotransplantation has predominantly focused on cardiac and renal applications, with no reported cases of porcine-to-human liver xenotransplantation. This study presents the world’s first successful genetically modified pig auxiliary liver xenotransplantation in a living human, achieving an unprecedented survival of 171 days, and provides valuable insights into the critical factors influencing the procedure’s success.