Researchers from the University at Albany and NYU Grossman School of Medicine have found a way to block a key cellular pathway known to drive chronic inflammation and impaired wound healing in people with diabetes.
The breakthrough could offer a new therapeutic option for stopping the harmful effects of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes at the source.
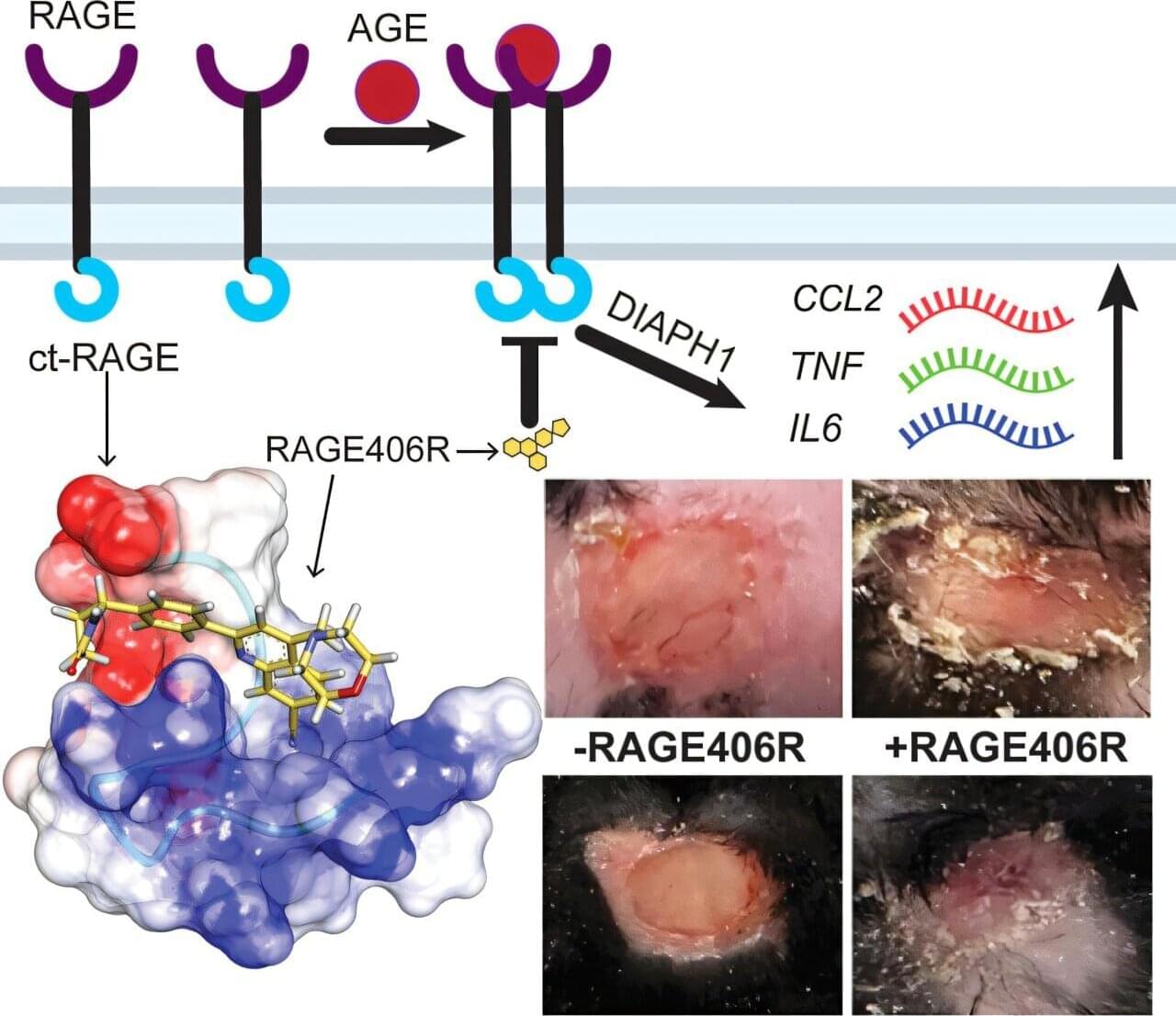
In their latest work, the researchers successfully identified—and developed a small molecule drug to disrupt—an intracellular chain reaction that is a major contributor to diabetes-induced complications. Their findings, published earlier this month, were featured on the cover of Cell Chemical Biology.