Dark matter is an elusive type of matter that does not emit, reflect or absorb light, yet is predicted to account for most of the universe’s mass. As it cannot be detected and studied using conventional experimental techniques, the nature and composition of dark matter have not yet been uncovered.
One of the most promising dark matter candidates (i.e., hypothetical particles that dark matter could be made of) are axions. Theory suggests that axions could convert into light particles (i.e., photons) under specific conditions, which could in turn generate signals that can be picked up by sophisticated equipment.
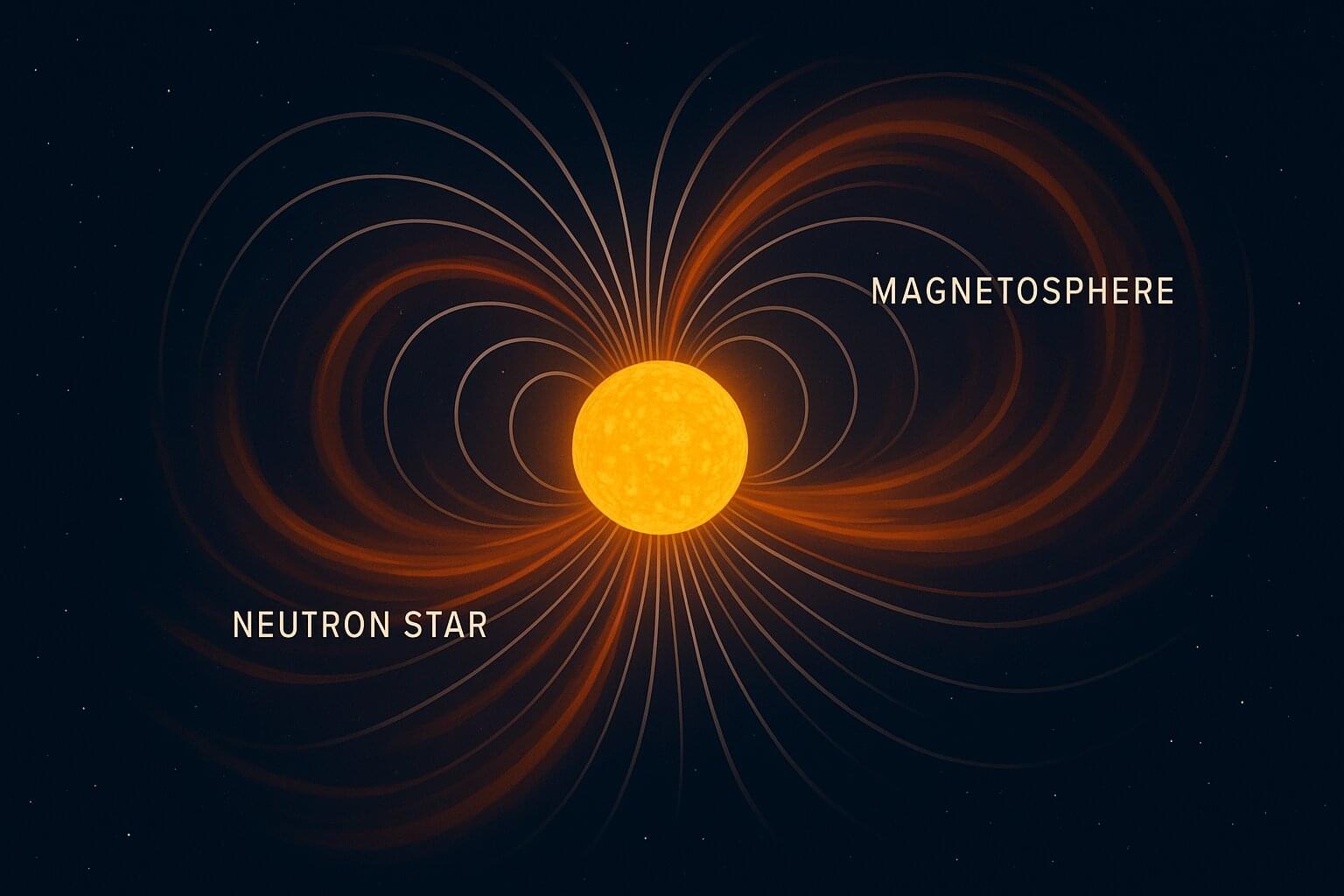
In strong magnetic fields, such as those surrounding neutron stars with large magnetic fields (i.e., magnetars), the conversion of axions into photons has been predicted to generate weak radio signals that could be detected using powerful Earth-based or space-based radio telescopes.