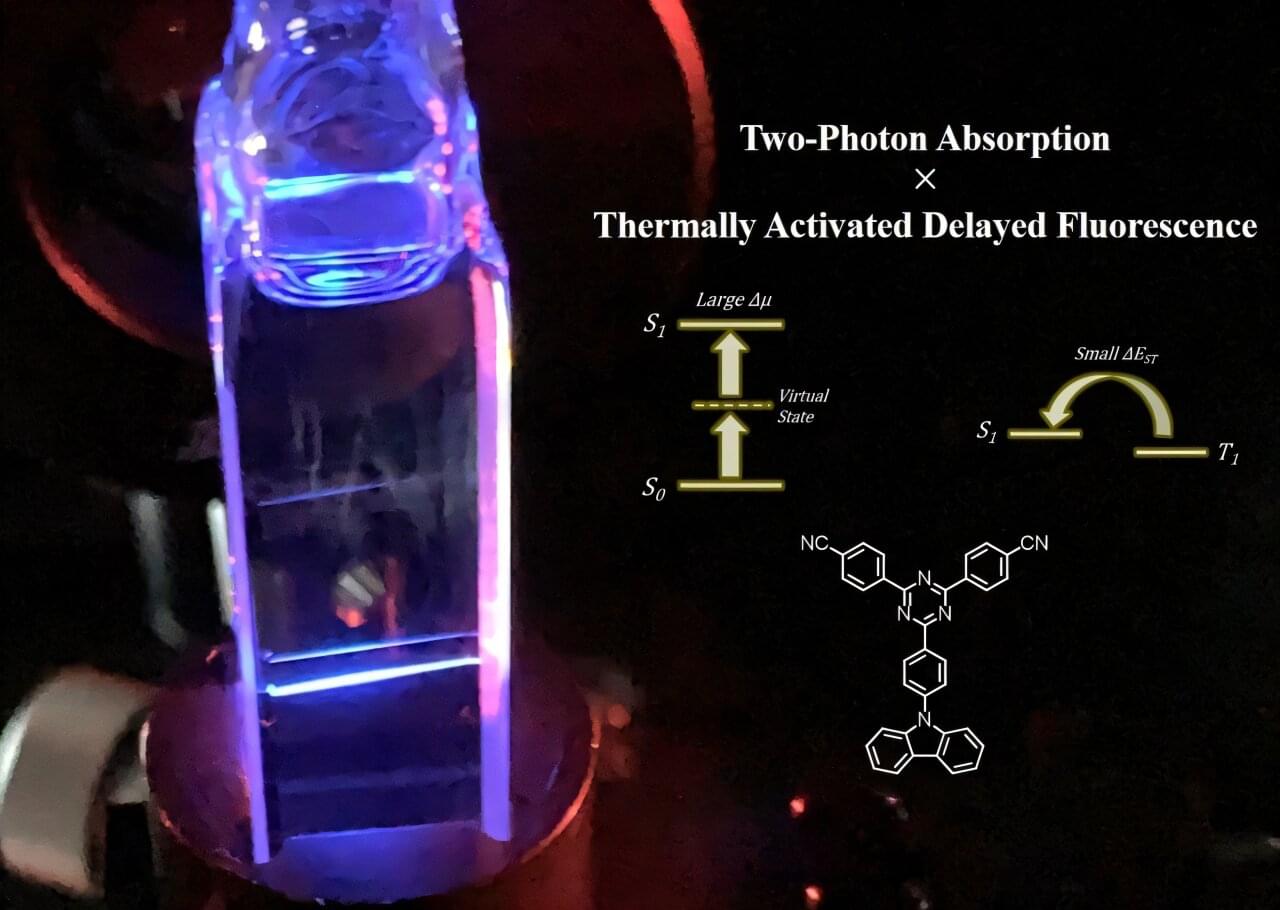
Researchers at Kyushu University have developed a novel organic molecule that simultaneously exhibits two highly sought-after properties: efficient light emission suitable for advanced displays and strong light absorption for deep-tissue bioimaging. This breakthrough addresses a long-standing challenge in molecular design, paving the way for next-generation multifunctional materials.
Their study, published online in the journal Advanced Materials on July 29, 2025, was conducted in collaboration with the National Taipei University of Technology and the National Central University.
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) are at the forefront of modern display and lighting technologies, powering nearly everything from smartphone screens to large televisions and monitors. A key phenomenon that is actively being researched to enhance OLED efficiency is thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF).