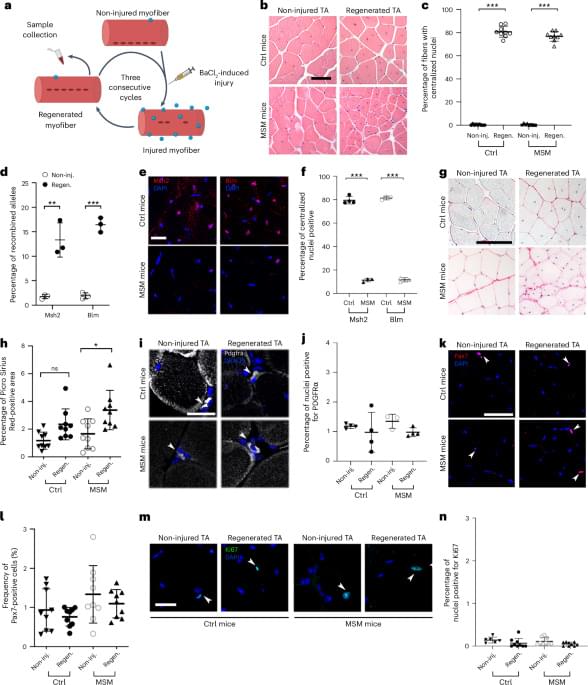
With aging, somatic mutations accumulate in cellular DNA; however, whether they drive age-related functional decline is incompletely understood. Here the authors show that these mutations can weaken muscle repair and reduce strength after injury, suggesting they play a role in age-related physical decline in mouse muscle.