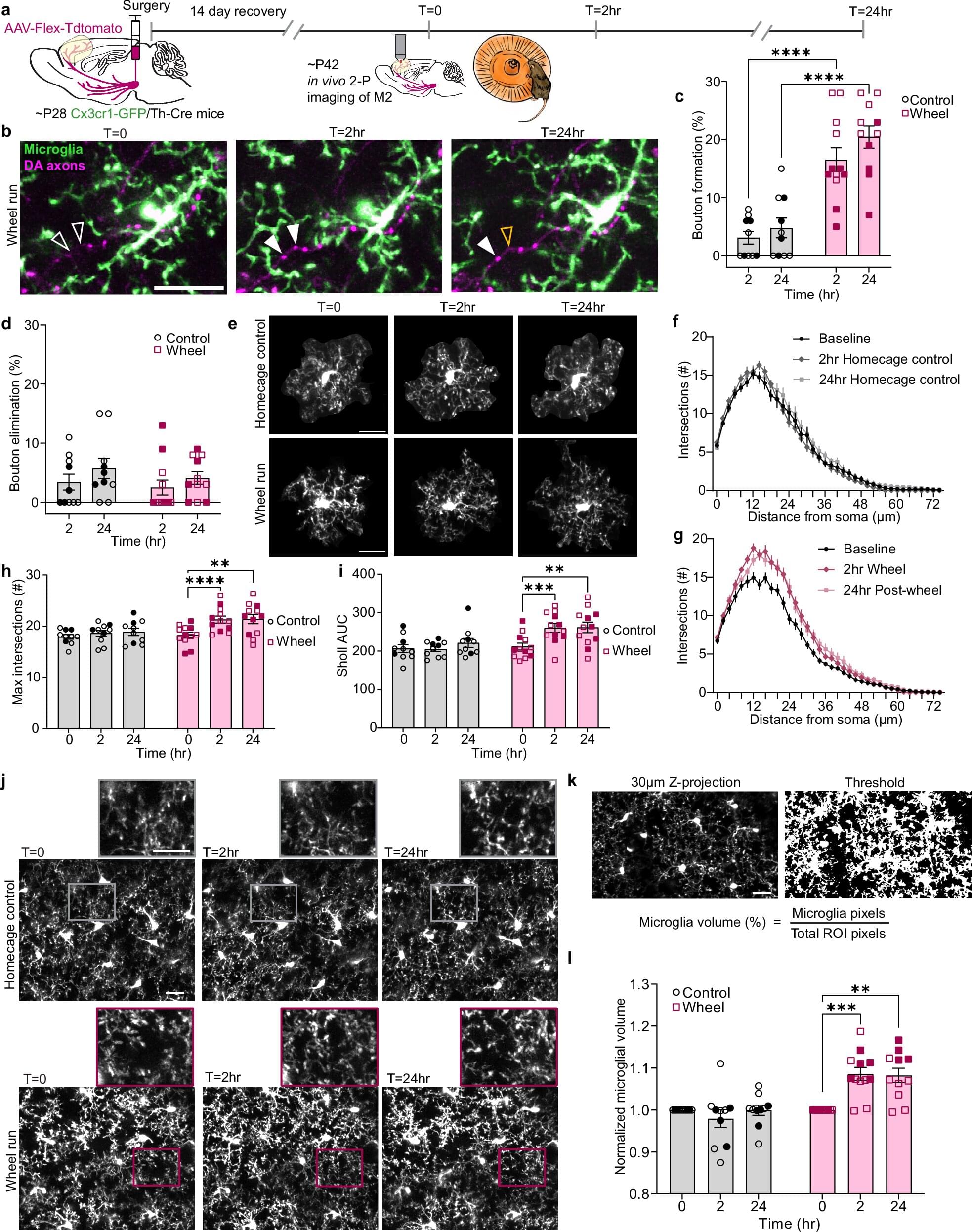
Making a smoothie, going for an evening walk, or having empathy for a loved one are all examples of executive functions that are controlled by the brain’s frontal cortex. This area of the brain goes through profound change throughout adolescence, and it is during this time that abnormalities in maturing circuits can set the stage for neurodevelopmental disorders, such as schizophrenia and ADHD.
Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester have discovered that microglia, the brain’s immune cells, play a key role in how the brain adapts to the changes in this area during adolescence, which may transform how neurodevelopmental disorders are treated during this window and, possibly, into adulthood.
“A better understanding of the ways we can drive changes in these circuits offers new targets for disease treatment,” said Rianne Stowell, Ph.D., research assistant professor of Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center, and first author of the study out today in Nature Communications.