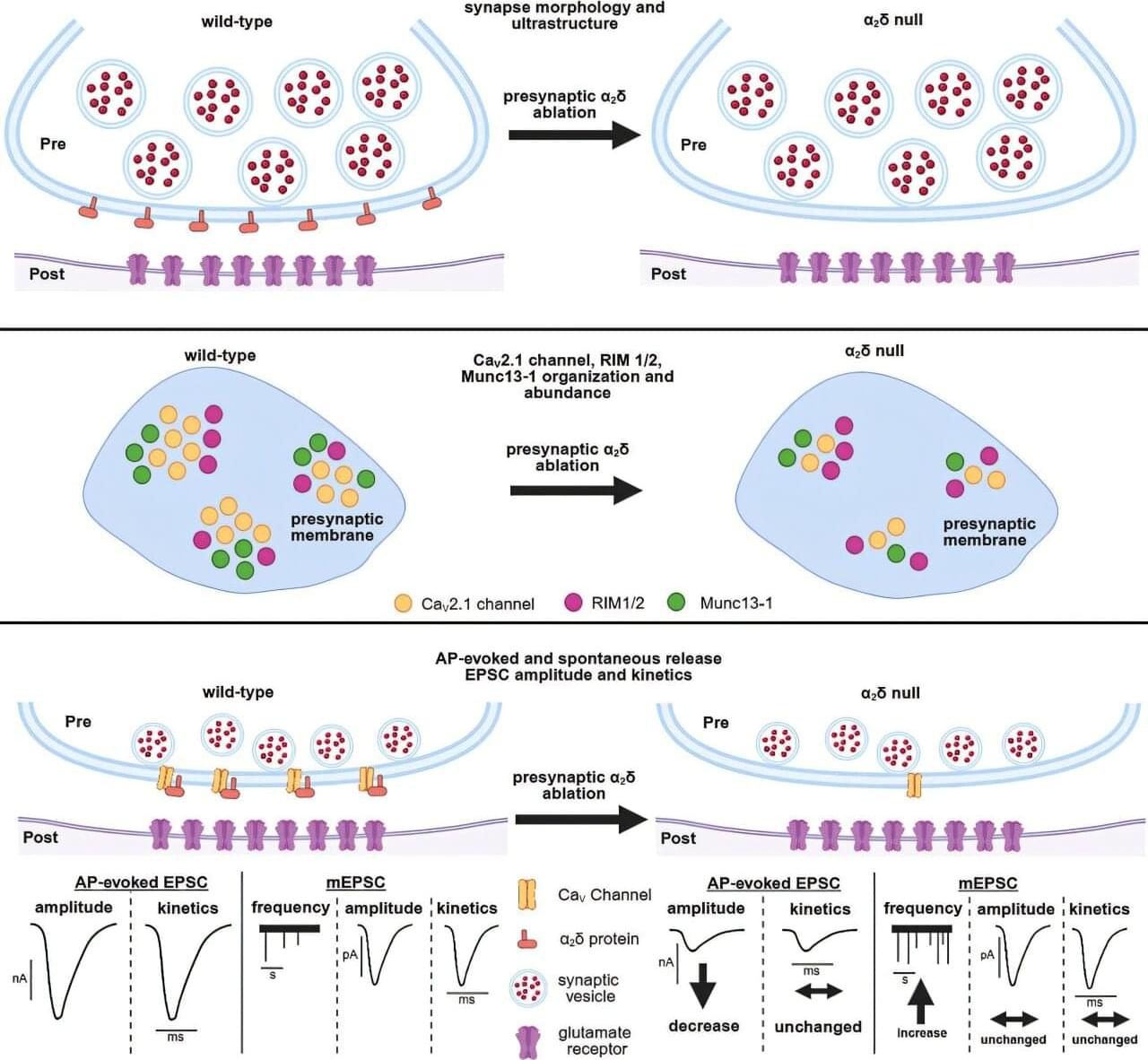
Cellular communication between neurons within our brain is complex and busy, much like a USPS mailroom.
To keep things running smoothly, the brain uses specialized molecules, termed alpha-2-delta (α2δ) proteins, to coordinate the sending and receival of signals between nerve cells in the brain.
Genetic variations in these types of proteins can impact important brain messaging and function, resulting in chronic pain, autism spectrum disorders, epilepsy, migraines, and other conditions.