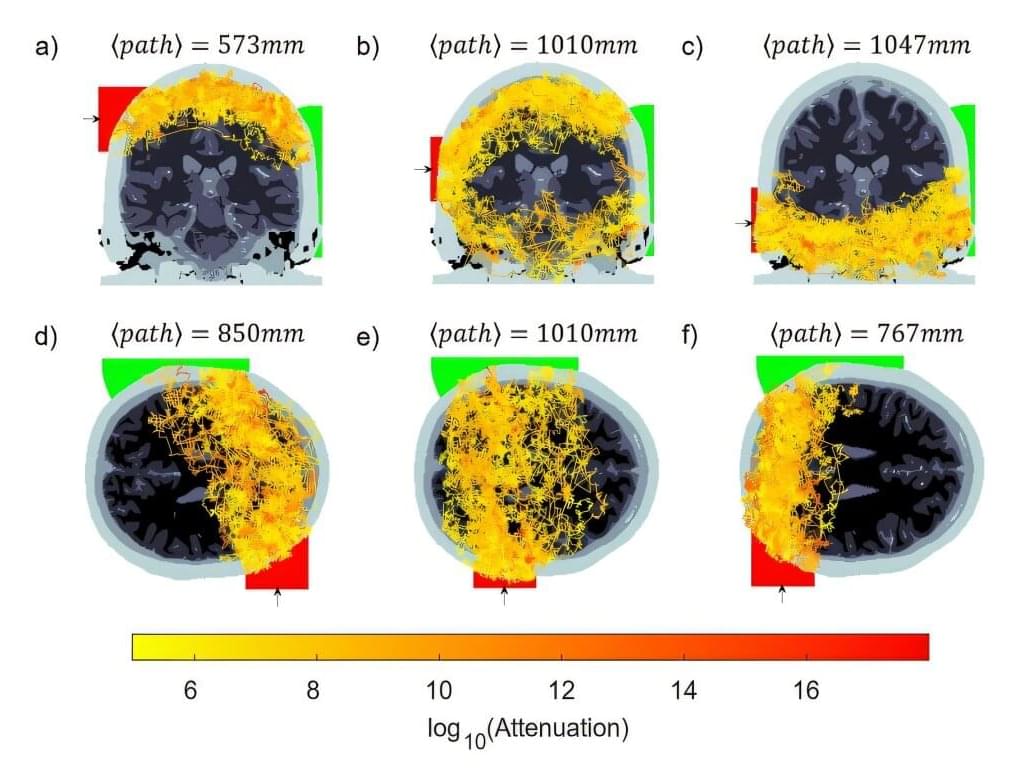
For decades, scientists have used near-infrared light to study the brain in a noninvasive way. This optical technique, known as fNIRS (functional near-infrared spectroscopy), measures how light is absorbed by blood in the brain, to infer activity.
Valued for portability and low cost, fNIRS has a major drawback: it can’t see very deep into the brain. Light typically only reaches the outermost layers of the brain, about 4 centimeters deep—enough to study the surface of the brain, but not deeper regions involved in critical functions like memory, emotion, and movement.
This drawback has restricted the ability to study deeper brain regions without expensive and bulky equipment like MRI machines.