An AI approach developed by researchers from the University of Sheffield and AstraZeneca, could make it easier to design proteins needed for new treatments.
In their study published in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence, Sheffield computer scientists in collaboration with AstraZeneca and the University of Southampton have developed a new machine learning framework that has shown the potential to be more accurate at inverse protein folding than existing state-of-the-art methods.
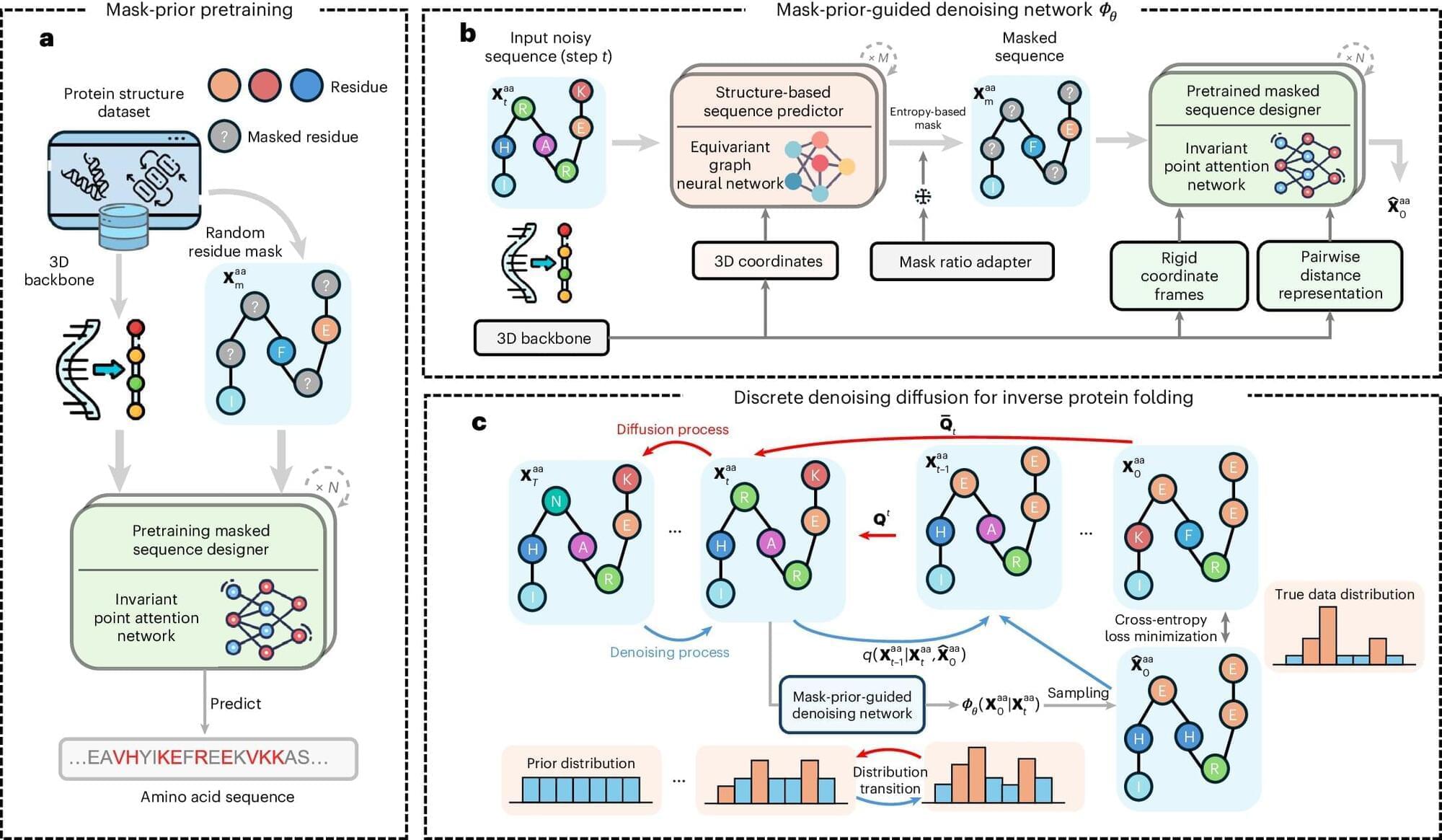
Inverse protein folding is a critical process for creating novel proteins. It is the process of identifying amino acid sequences, the building blocks of proteins, that fold into a desired 3D protein structure and enable the protein to perform specific functions.