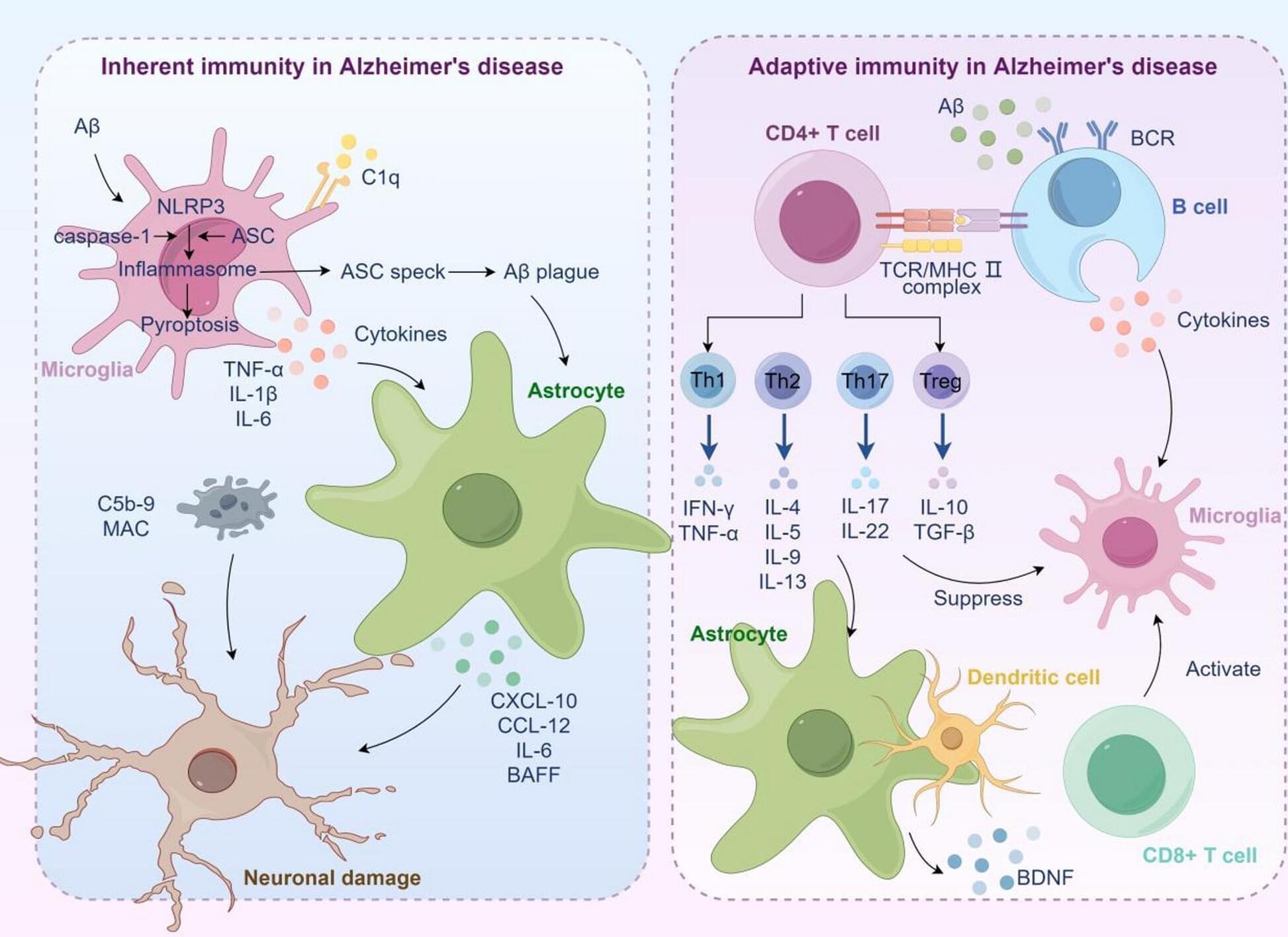
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by macroscopic features such as cortical atrophy, narrowing of the gyri, widening of the sulci, and enlargement of the ventricles. At the cellular level, the pathological characteristics include the extracellular aggregation of β-amyloid (Aβ) forming senile plaques, and the intracellular accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau proteins forming neurofibrillary tangles. AD leads to the progressive decline of cognitive, behavioral, and social abilities, with no effective treatment available currently. The pathophysiology of AD is complex, involving mechanisms such as immune dysregulation and lipid metabolism alterations. Immune cells, such as microglia, can identify and clear pathological aggregates like Aβ early in the disease.