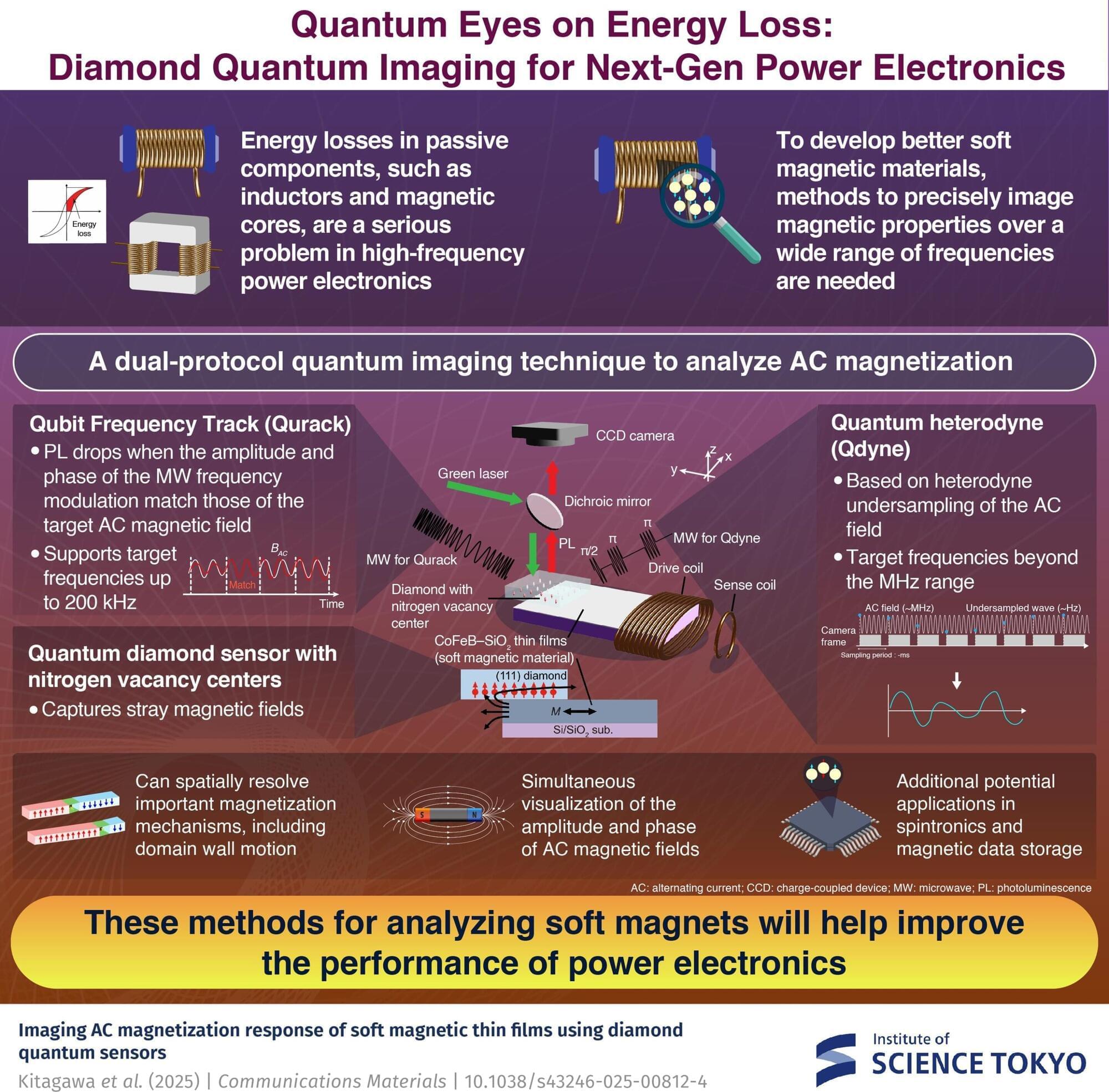
Improving energy conversion efficiency in power electronics is vital for a sustainable society, with wide-bandgap semiconductors like GaN and SiC power devices offering advantages due to their high-frequency capabilities. However, energy losses in passive components at high frequencies hinder efficiency and miniaturization. This underscores the need for advanced soft magnetic materials with lower energy losses.
In a study published in Communications Materials, a research team led by Professor Mutsuko Hatano from the School of Engineering, Institute of Science, Tokyo, Japan, has developed a novel method for analyzing such losses by simultaneously imaging the amplitude and phase of alternating current (AC) stray fields, which are key to understanding hysteresis losses.
Using a diamond quantum sensor with nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers and developing two protocols—qubit frequency tracking (Qurack) for kHz and quantum heterodyne (Qdyne) imaging for MHz frequencies—they realized wide-range AC magnetic field imaging. This study was carried out in collaboration with Harvard University and Hitachi, Ltd.