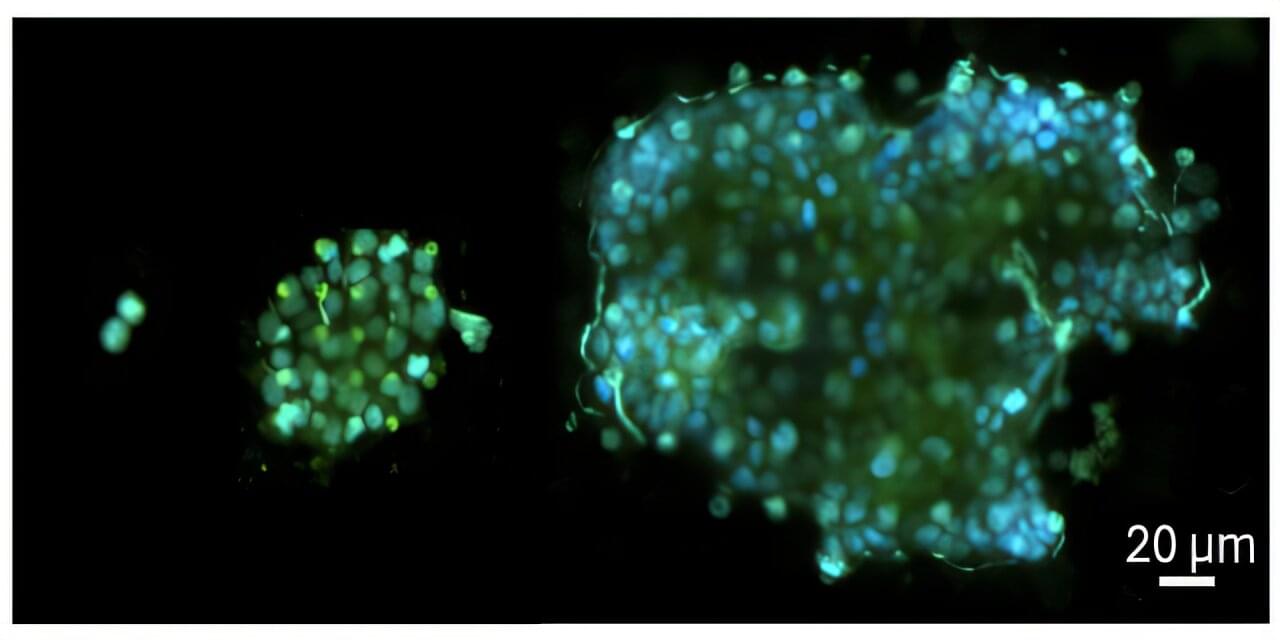
A McGill University-led research collaboration has achieved a breakthrough in understanding how cancer spreads. A clinical study of ovarian and colorectal cancer patients found cancer cells move in the bloodstream in clusters more commonly than was previously thought. The discovery could help doctors more quickly identify which cancer patients are at high risk of having their cancer spread to other organs, knowledge that could guide treatment decisions. The findings also potentially open new avenues for treatment.
The study, published in Communications Medicine, was conducted with researchers and clinicians Anne-Marie Mes-Masson and Dr. Diane Provencher at the Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Dr. Peter Metrakos at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre and Luke McCaffrey at the McGill-affiliated Rosalind and Morris Goodman Cancer Institute.
Cancer is responsible for about 1 in 4 deaths in Canada. In most cases, it is not the original tumor that proves fatal, but the cancer spreading to other organs, a process called metastasis. This occurs when circulating tumor cells (CTCs) break away from tumors, enter the bloodstream, and seed new tumors elsewhere in the body. On rare occasions, CTCs break away as a group of cells sticking to one another and forming a cluster.