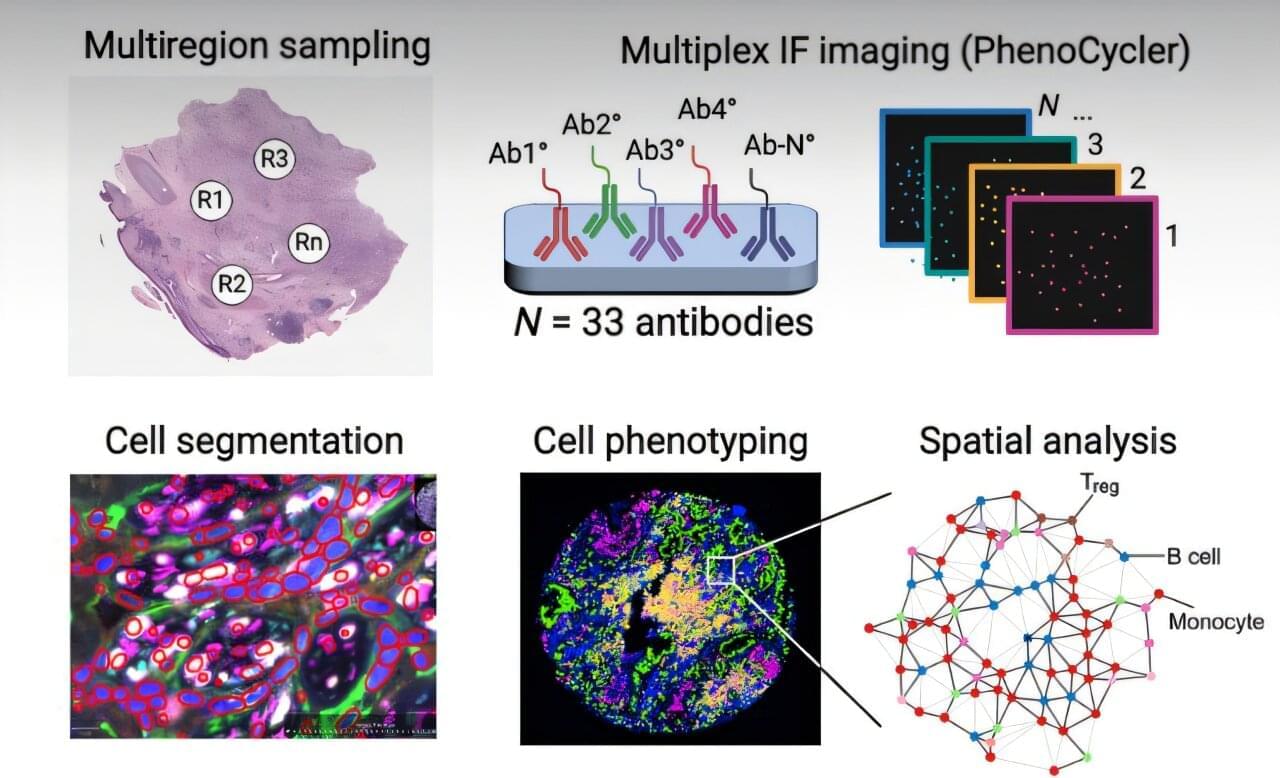
Amidst the continued struggle to treat non-small-cell lung cancer, a new study led by Stanford University scientists suggests that a patient’s response to immunotherapy may hinge on how immune cells cluster around tumors. Their results reveal that spatial arrangements of certain immune cells within tumors can serve as powerful predictors of treatment response, surpassing existing biomarker tests.
Lung cancer leads global cancer mortality, and non-small-cell variants make up more than 80% of cases. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have transformed therapy yet help only 27–45% of recipients.
Reliable predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy response have eluded clinicians, who currently rely on PD-L1 immunohistochemistry, tumor mutational burden, and microsatellite stability tests, each offering modest predictive performance across trials and are prone to inconsistency.