At the level of molecules and cells, ketamine and dexmedetomidine work very differently, but in the operating room they do the same exact thing: anesthetize the patient. By demonstrating how these distinct drugs achieve the same result, a new study in animals by neuroscientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT identifies a potential signature of unconsciousness that is readily measurable to improve anesthesiology care.
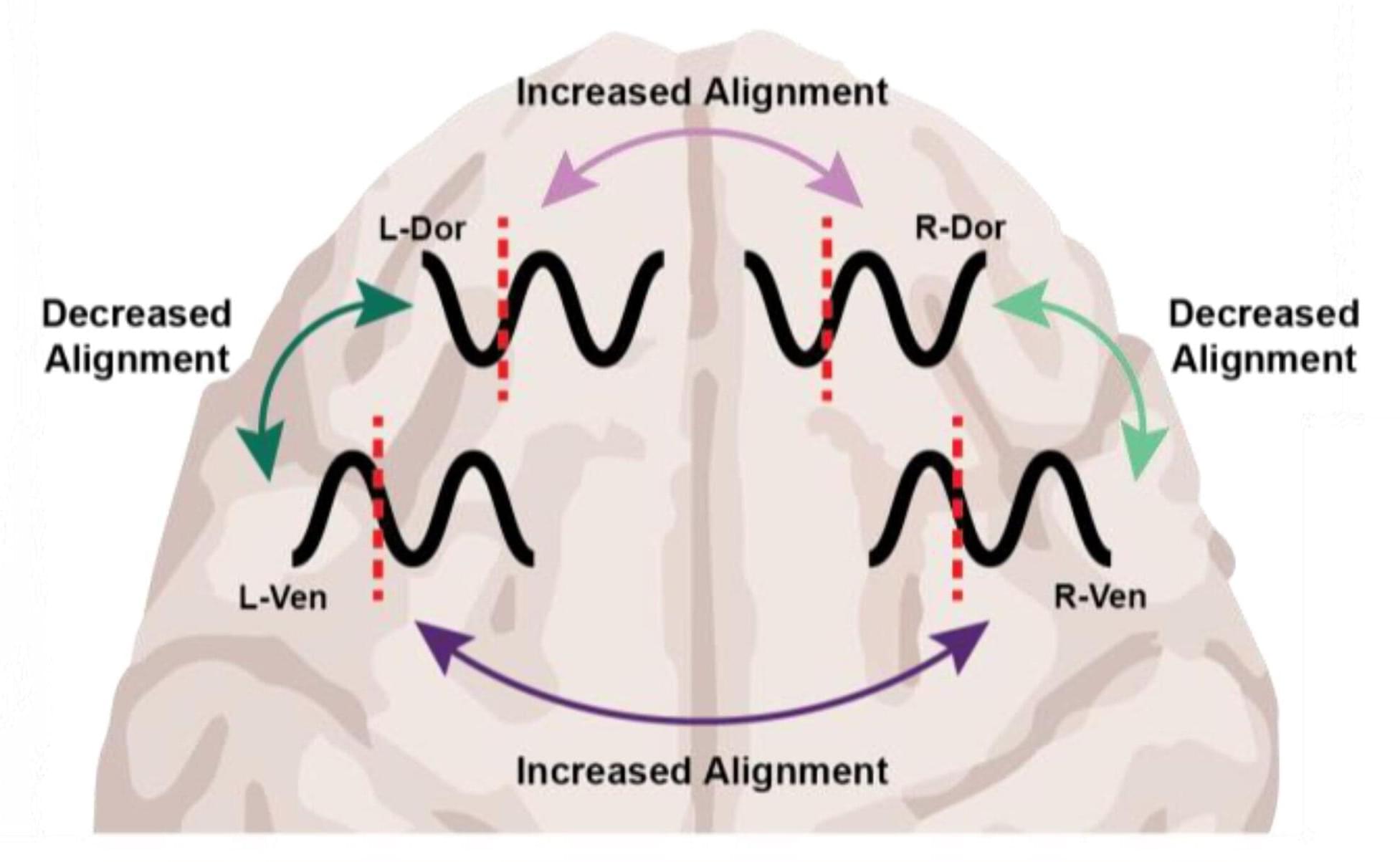
What the two drugs have in common, the researchers discovered, is the way they push around brain waves, which are produced by the collective electrical activity of neurons.
When brain waves are in phase, meaning the peaks and valleys of the waves are aligned, local groups of neurons in the brain’s cortex can share information to produce conscious cognitive functions such as attention, perception and reasoning, said Picower Professor Earl K. Miller, senior author of the new study in Cell Reports. When brain waves fall out of phase, local communications, and therefore functions, fall apart, producing unconsciousness.