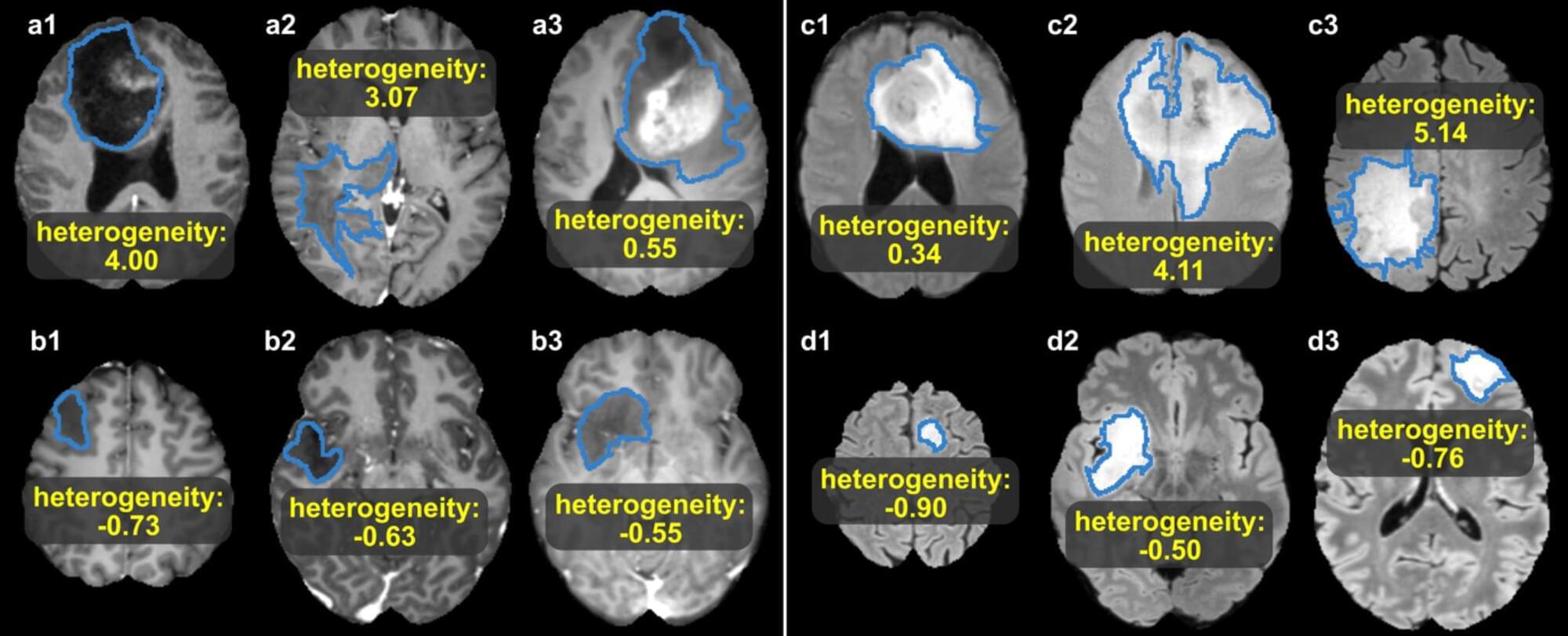
Purpose Adult patients with diffuse lower-grade gliomas (dLGG) show heterogeneous survival outcomes, complicating postoperative treatment planning. Treating all patients early increases the risk of long-term side effects, while delayed treatment may lead to impaired survival. Refinement of prognostic models could optimize timing of treatment. Conventional radiological features are prognostic in dLGG, but MRI could carry more prognostic information. This study aimed to investigate MRI-based radiomics survival models and compare them with clinical models. Methods Two clinical survival models were created: a preoperative model (tumor volume) and a full clinical model (tumor volume, extent of resection, tumor subtype). Radiomics features were extracted from preoperative MRI. The dataset was divided into training set and unseen test set (70:30). Model performance was evaluated on test set with Uno’s concordance index (c-index). Risk groups were created by the best performing model’s predictions. Results 207 patients with mutated IDH (mIDH) dLGG were included. The preoperative clinical, full clinical and radiomics models showed c-indexes of 0.70, 0.71 and 0.75 respectively on test set for overall survival. The radiomics model included four features of tumor diameter and tumor heterogeneity. The combined full clinical and radiomics model showed best performance with c-index = 0.79. The survival difference between high- and low-risk patients according to the combined model was both statistically significant and clinically relevant. Conclusion Radiomics can capture quantitative prognostic information in patients with dLGG. Combined models show promise of synergetic effects and should be studied further in astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma patients separately for optimal modelling of individual risks.