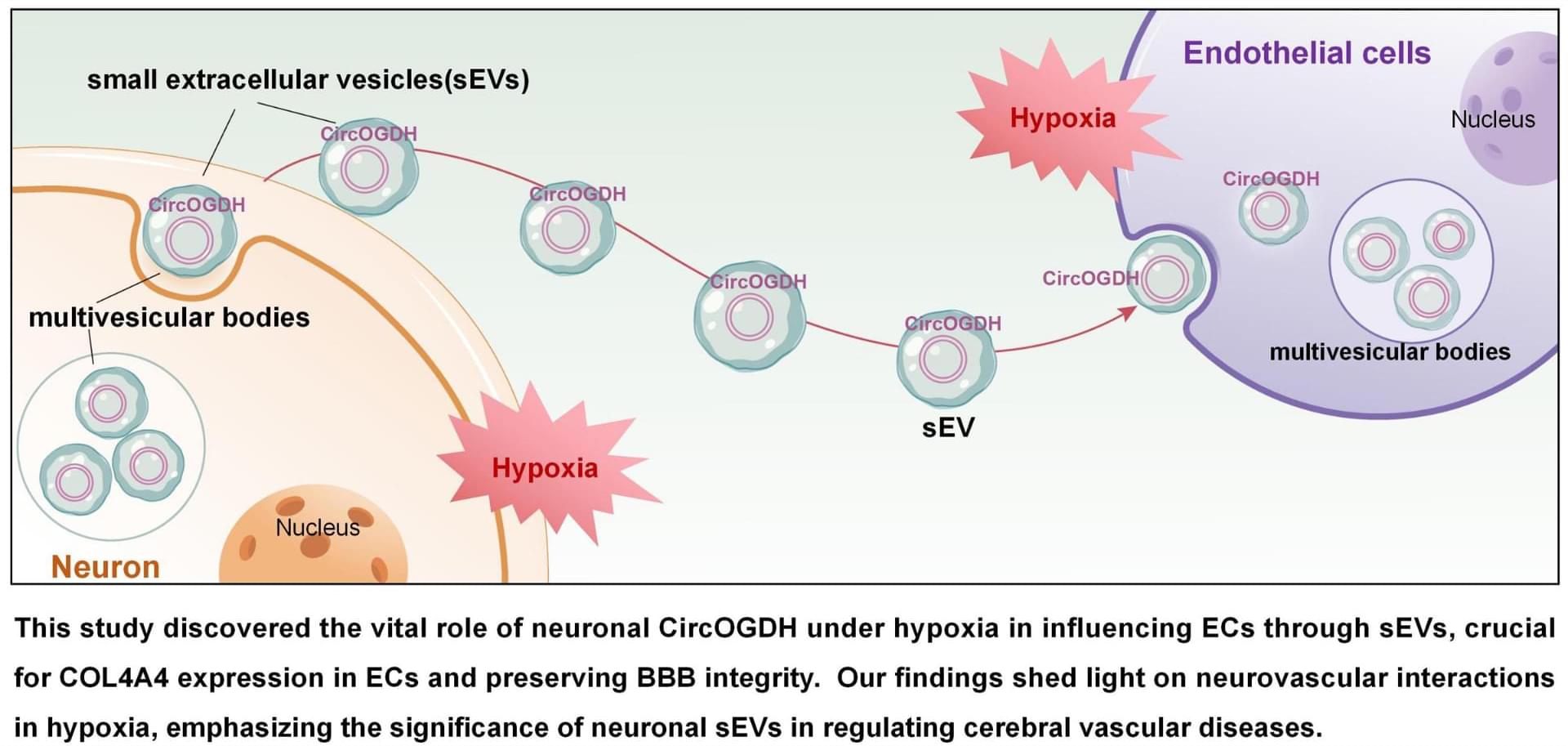
STROKE: Hypoxia induces neuronal release of CircOGDH in small extracellular vesicles to interact with endothelial cells for enhancing blood-brain barrier repair during acute ischemic stroke.
BACKGROUND: Acute ischemic stroke disrupts communication between neurons and blood vessels in penumbral areas. How neurons and blood vessels cooperate to achieve blood-brain barrier repair remains unclear. Here, we reveal crosstalk between ischemic penumbral neurons and endothelial cells (ECs) mediated by circular RNA originating from oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (CircOGDH). METHODS: We analyzed clinical data from patients with acute ischemic stroke to explore the relationship between CircOGDH levels and hemorrhagic transformation events. In addition, a middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion mouse model with neuronal CircOGDH suppression was used to assess endothelial permeability.