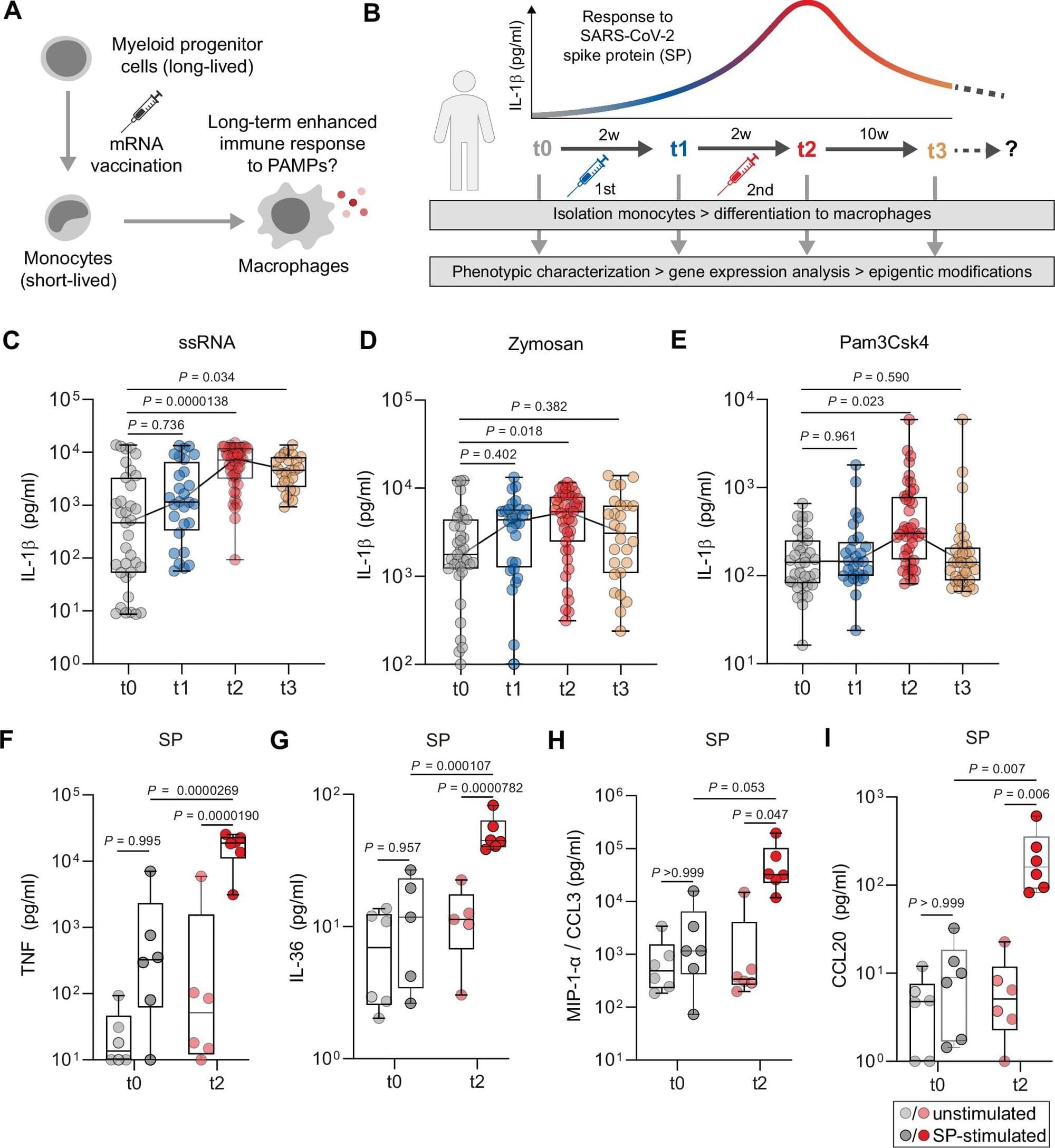
Researchers at the University of Cologne and University Hospital Cologne have determined that the novel mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines not only induce acquired immune responses such as antibody production, but also cause persistent epigenetic changes in innate immune cells.
The study, “Persistent epigenetic memory of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in monocyte-derived macrophages,” led by Professor Dr. Jan Rybniker, who heads the Division of Infectious Diseases at University Hospital Cologne and is a principal investigator at the Center for Molecular Medicine Cologne (CMMC), and Dr. Robert Hänsel-Hertsch, principal investigator at the CMMC, was published in Molecular Systems Biology.
The immune system comprises two immunity strategies: the innate and the acquired (adaptive) immune system. The innate immune system provides general protection from pathogens and must react quickly. The adaptive immune system adapts to new pathogens and is highly specific in its response. Both systems work closely together.