Plants are susceptible to a wide range of pathogens. For the common potato plant, one such threat is Pectobacterium atrosepticum, a bacterium that causes stems to blacken, tissues to decay, and often leads to plant death, resulting in significant agricultural losses each year.
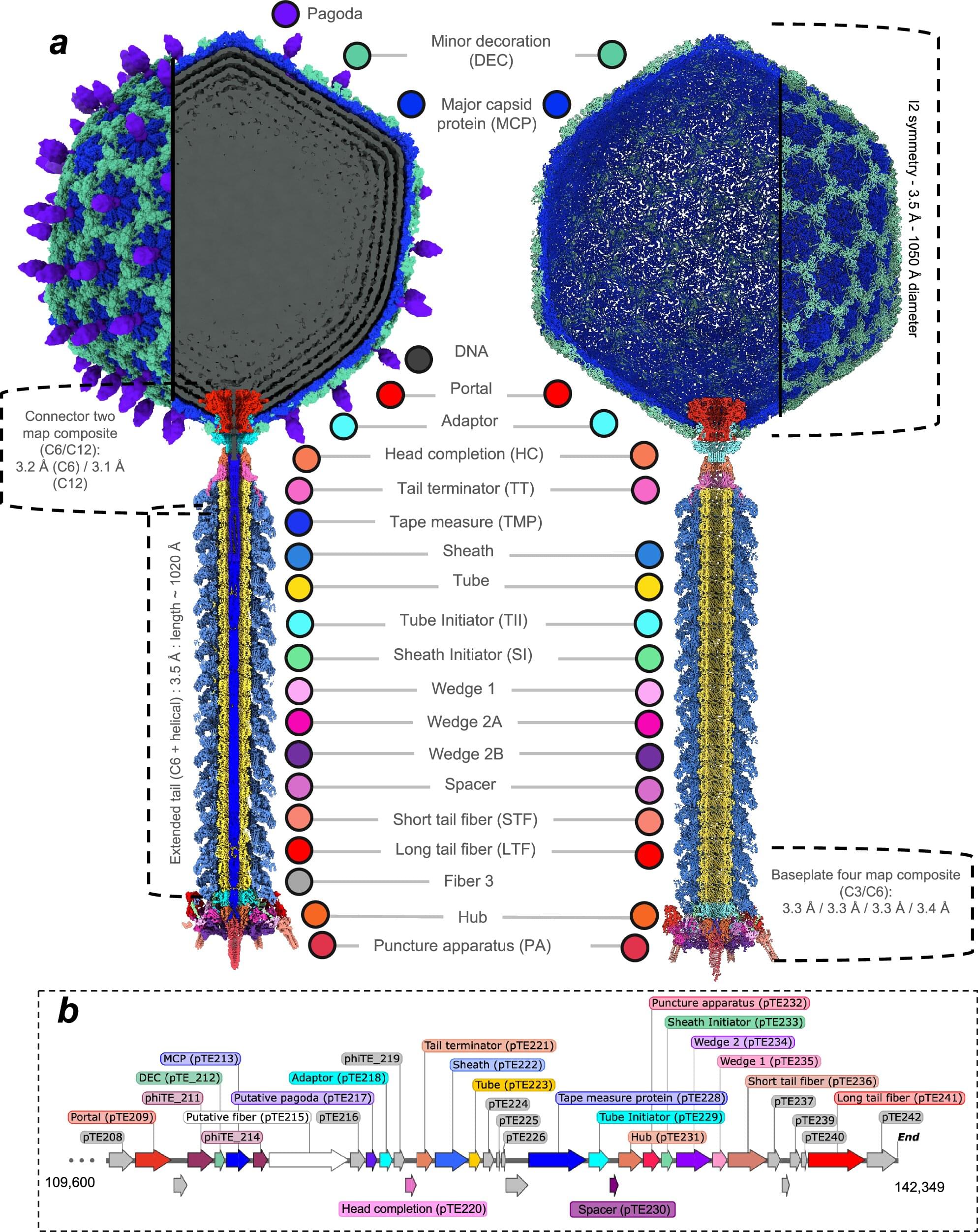
In 2012, researchers isolated a new virus that infects and kills this bacterium—a bacteriophage named φTE (phiTE). Now, for the first time, scientists have uncovered the atomic structure of φTE, revealing a possible mechanism of infection that may be more complex than previously thought.
The study, published earlier this month in Nature Communications, is the result of a multidisciplinary collaboration between researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and the University of Otago. It brings together expertise across several fields, including virology, structural biology, molecular genetics, protein engineering, biochemistry, and biophysics.