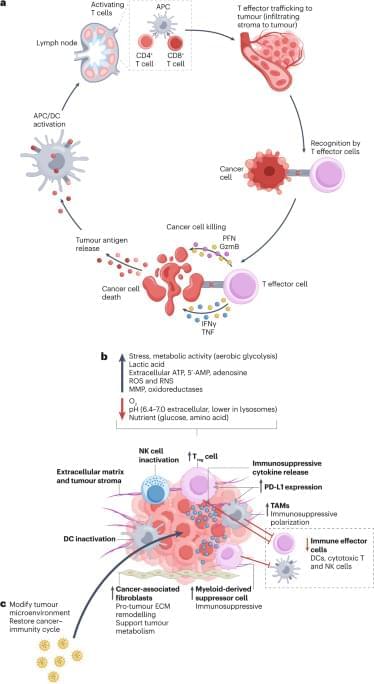
Immunotherapies, predominantly immune-checkpoint inhibitors and chimaeric antigen receptor T cells, have transformed oncology. Nonetheless, these systemically administered agents have several limitations, including the risk of off-target toxicities and a lack of activity owing to an inability to overcome an immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment (TME). In this Review, the authors describe the potential to overcome these challenges using functionalized nanomaterials that are designed to release a wide range of immunotherapeutic cargoes in response to specific TME characteristics, including hypoxia, differences in pH, the presence of specific enzymes, reactive oxygen species and/or high levels of extracellular ATP.