Combinatorial optimization problems (COPs) arise in various fields such as shift scheduling, traffic routing, and drug development. However, they are challenging to solve using traditional computers in a practical timeframe.
Alternatively, annealing processors (APs), which are specialized hardware for solving COPs, have gained significant attention. They are based on the Ising model, in which COP variables are presented as magnetic spins and constraints as interactions between spins. Solutions are obtained by finding the spin state that minimizes the energy of the system.
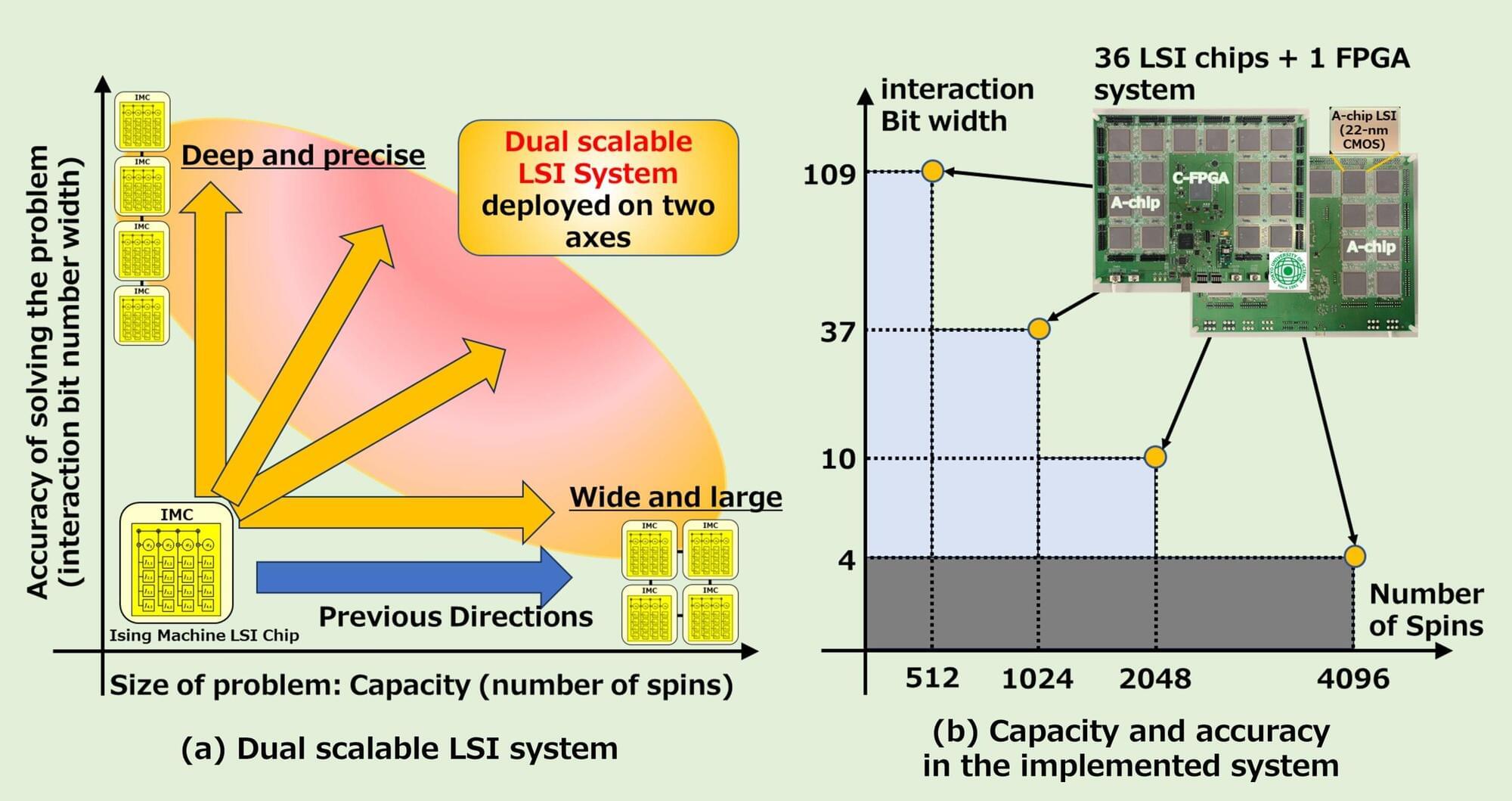
There are two types of Ising models, the sparsely-coupled model and the fully-coupled model. Sparsely-coupled models offer high scalability by allowing more spins, but require COPs to be transformed to fit the model. Fully-coupled models, on the other hand, allow any COP to be mapped directly without transformation, making them highly desirable.