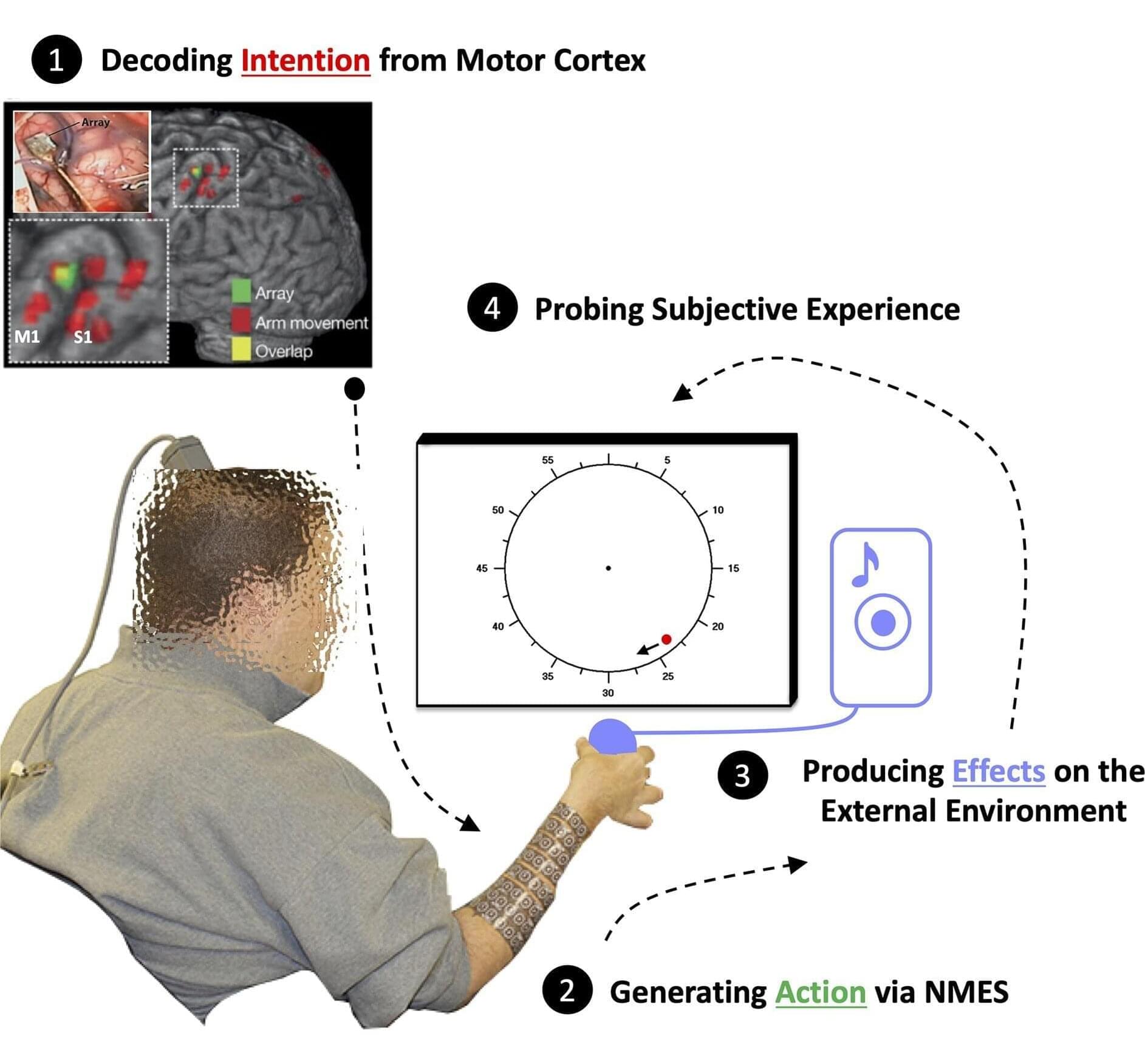
Researchers led by Jean-Paul Noel at the University of Minnesota, United States, have decoupled intentions, actions and their effects by manipulating the brain-machine interface that allows a person with otherwise paralyzed arms and legs to squeeze a ball when they want to.
Published in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, the study reveals temporal binding between intentions and actions, which makes actions seem to happen faster when they are intentional.
Separating intentions from actions was made possible because of a brain-machine interface. The participant was paralyzed with damage to their C4/C5 vertebrae and had 96 electrodes implanted in the hand region of their motor cortex.