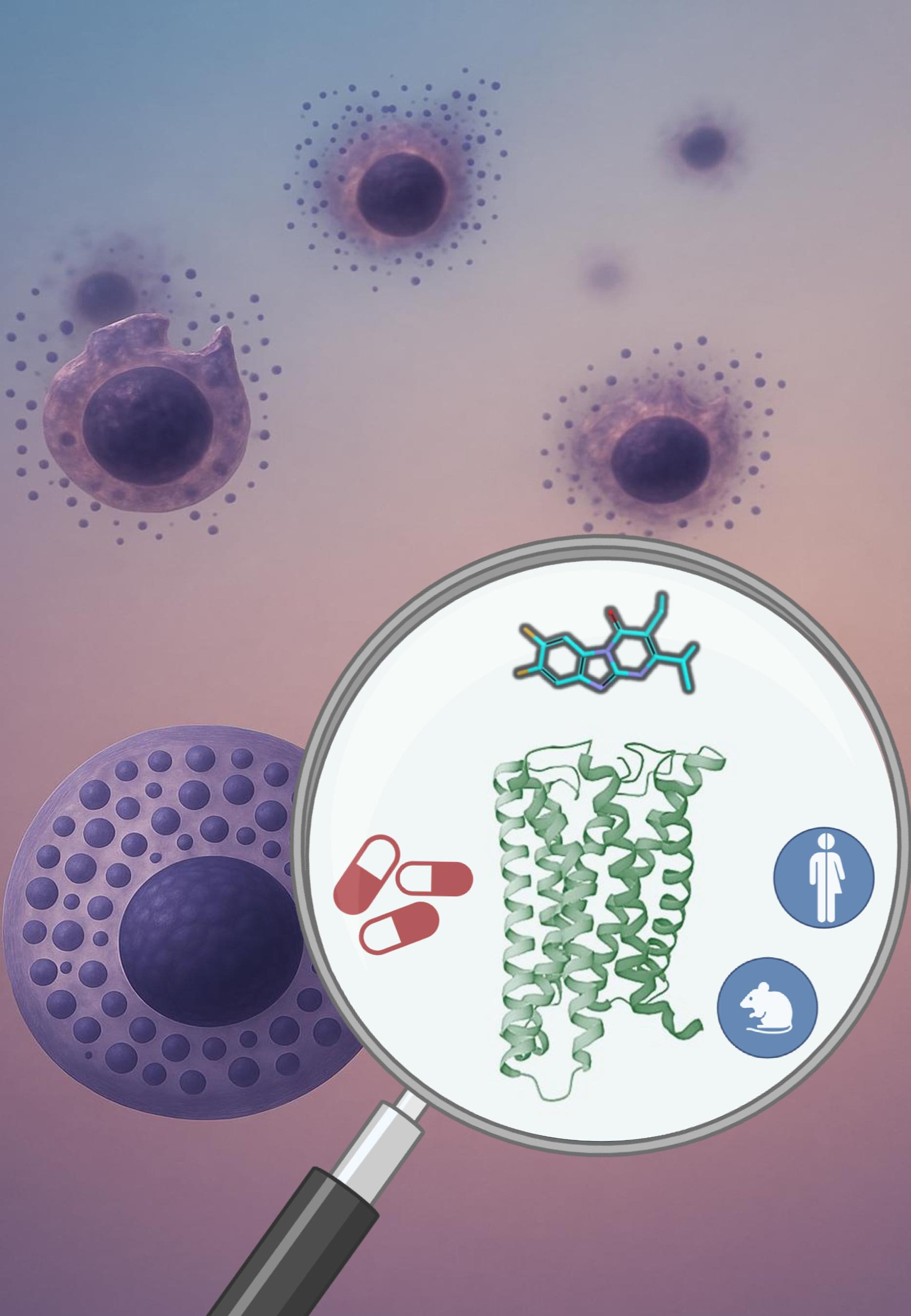
Irritable bowel syndrome, chronic itching, asthma and migraine are in many cases hard-to-treat conditions. They have in common that they are triggered by an excessive immune response—which in severe cases can be life-threatening.
A team of researchers led by the University of Bonn has now identified a promising bioactive compound that could effectively reduce symptoms and slash fatality risk. The compound blocks a receptor on certain defense cells, thus preventing a derailed immune response. The study findings have been published in the journal Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.
If you have ever been bitten by a mosquito, you will know how annoying the resulting itching can be. This is in large part due to mast cells— immune cells found in the skin and mucous membranes that are full of inflammatory messengers. When a person is bitten, antibodies bind to substances in the mosquito’s saliva, and this complex can activate the mast cells, which then release their payload all at once. This leads to the symptoms of redness, swelling and itching, which usually subside after a short while, or even quicker, using the right ointment.