Mitochondria play a crucial role in maintaining energy balance and cellular health. Recent studies have shown that chronic stress in neuronal mitochondria can have far-reaching effects, not only damaging the neurons themselves but also influencing other tissues and systemic metabolic functions.
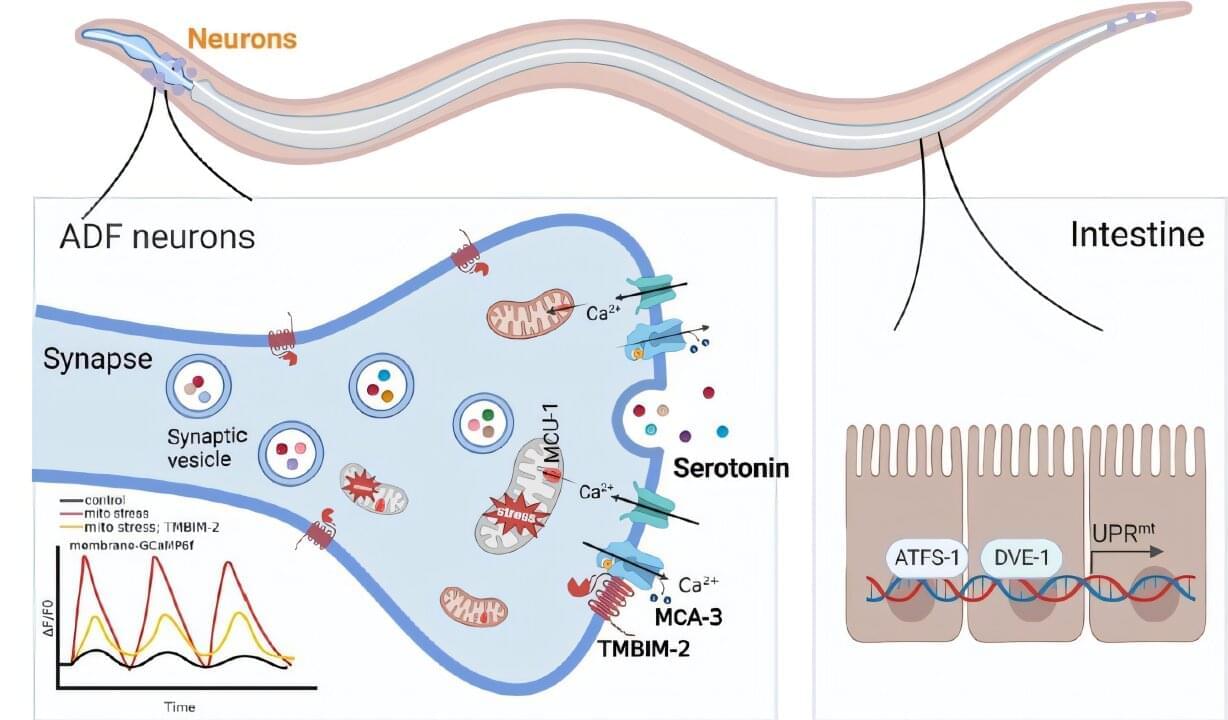
A new study led by Dr. Tian Ye’s research team at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reveals that chronic mitochondrial stress in neurons promotes serotonin release via TMBIM-2-dependent calcium (Ca²⁺) oscillations, which in turn activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) in the intestine. The findings are published in the Journal of Cell Biology.
The researchers found that TMBIM-2 works in coordination with the plasma membrane calcium pump MCA-3 (a PMCA homolog) to regulate synaptic Ca²⁺ balance, sustaining persistent calcium signaling oscillations at neuronal synaptic sites.