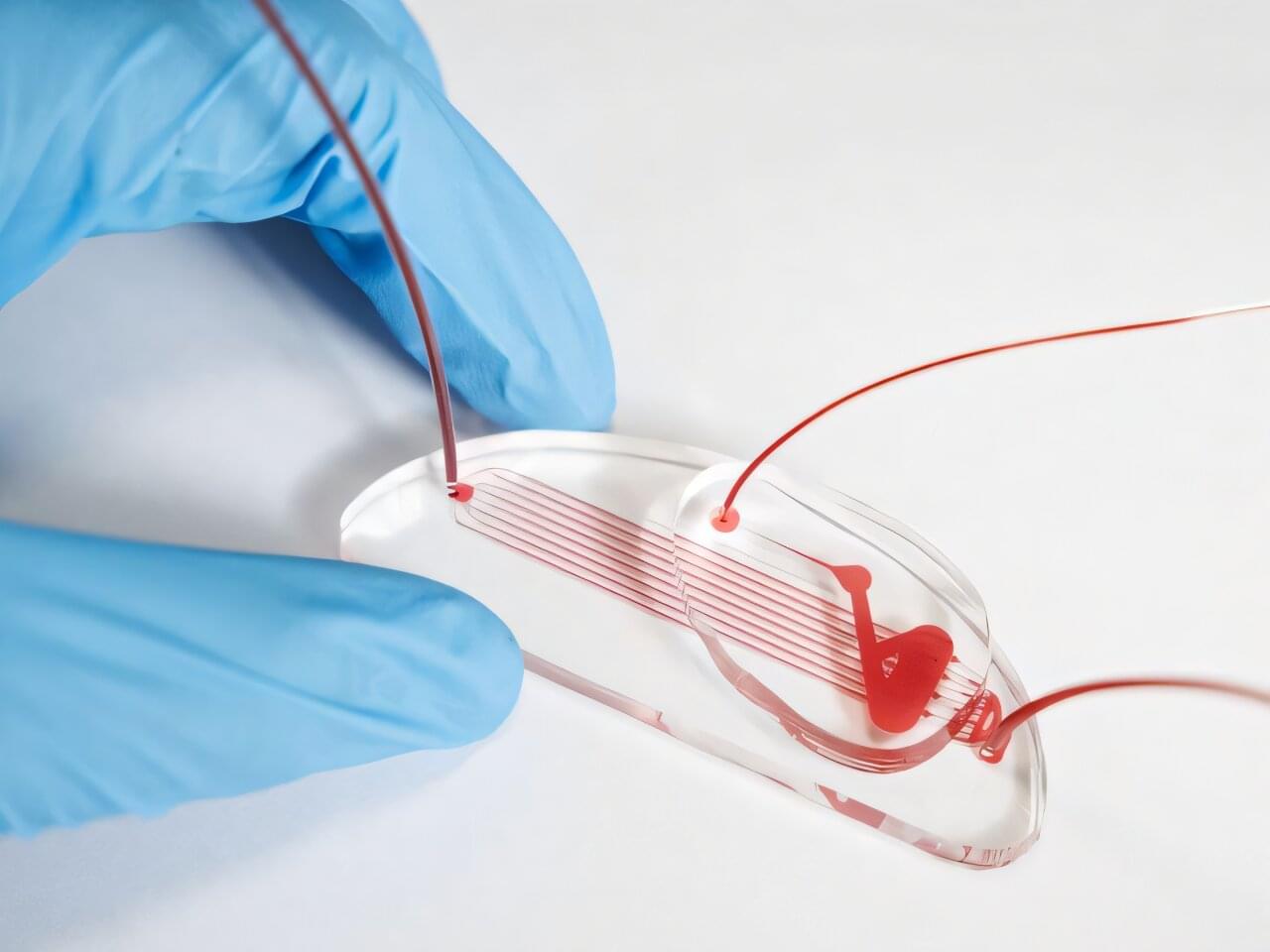
Researchers at the University of Houston, in collaboration with Baylor College of Medicine, are developing new devices for treating children with hyperleukocytosis, a condition that develops when the body has an extremely high number of white blood cells, often due to leukemia.
Leukemia is the most common type of cancer in children, with an annual incidence of about 5 per 100,000 children in the United States. Up to 20–30% of patients with acute leukemia develop hyperleukocytosis, placing them at risk for life-threatening complications.
Although definitive treatment for acute leukemia involves chemotherapy, leukapheresis—to urgently reduce dangerously elevated white blood cell counts—is a potentially life-saving therapeutic option. During leukapheresis, a large machine uses centrifugation to separate white blood cells, or leukocytes, from the rest of the blood, which is then returned to the patient.