Adding immunotherapy to a new type of inhibitor that targets multiple forms of the cancer-causing gene mutation KRAS kept pancreatic cancer at bay in preclinical models for significantly longer than the same targeted therapy by itself, according to researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center. The results, published in Cancer Discovery, prime the combination strategy for future clinical trials.
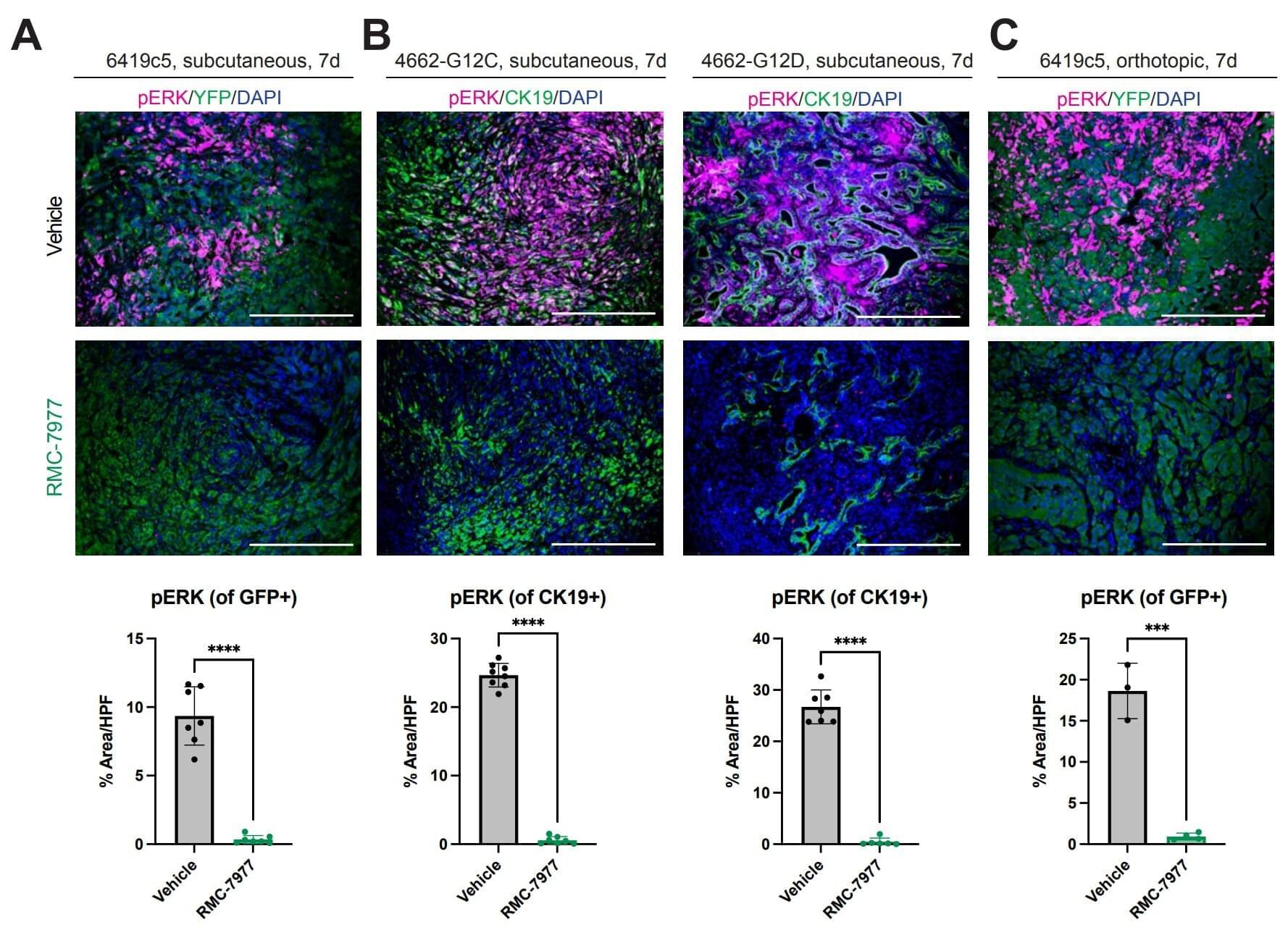
Patients with pancreatic cancer have an overall poor prognosis: in most patients, the disease has already spread at the time of diagnosis, resulting in limited treatment options. Nearly 90 percent of pancreatic cancers are driven by KRAS mutations, the most common cancer-causing gene mutation across cancer types, which researchers long considered “undruggable.”
In 2021, the first KRAS inhibitor was approved to treat non-small cell lung cancer with KRAS G12C mutations, but with longer follow-up, it has become clear that KRAS-mutant cancers can quickly evolve to resist therapies targeted at one specific form of the gene mutation.