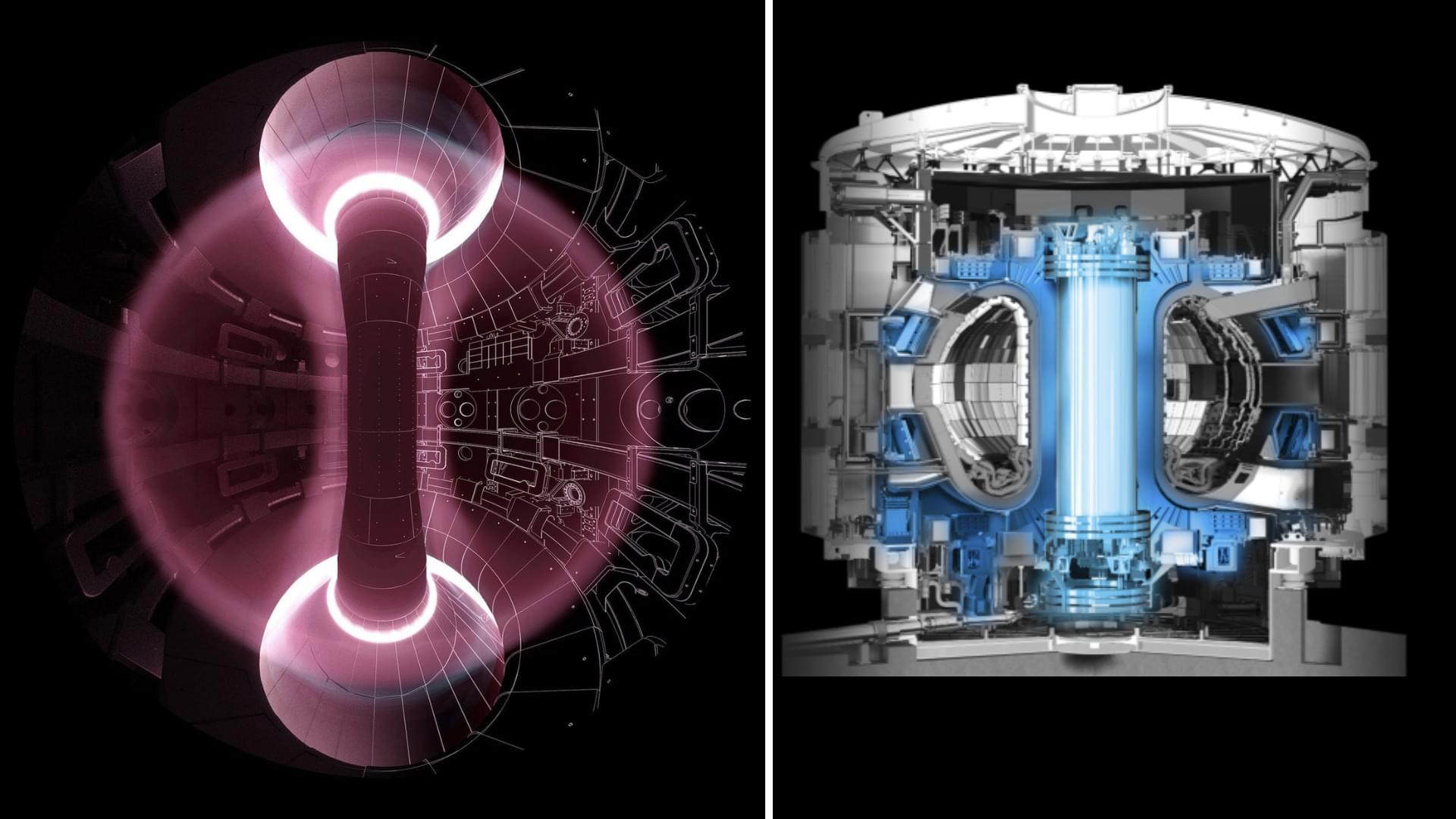
The advancement can enable turbulent analysis of entire nuclear fusion reactors.
“By utilizing deep learning on GPUs, we have reduced computation time by a factor of 1,000 compared to traditional CPU-based codes,” said the joint research team.
“This advancement represents a cornerstone for digital twin technologies, enabling turbulent analysis of entire nuclear fusion reactors or replicating real Tokamaks in a virtual computing environment.”
Researchers underlined that the proposed FPL-net can solve the FPL equation in a single step, achieving results 1,000 times faster than previous methods with an error margin of just one-hundred-thousandth, demonstrating exceptional accuracy.