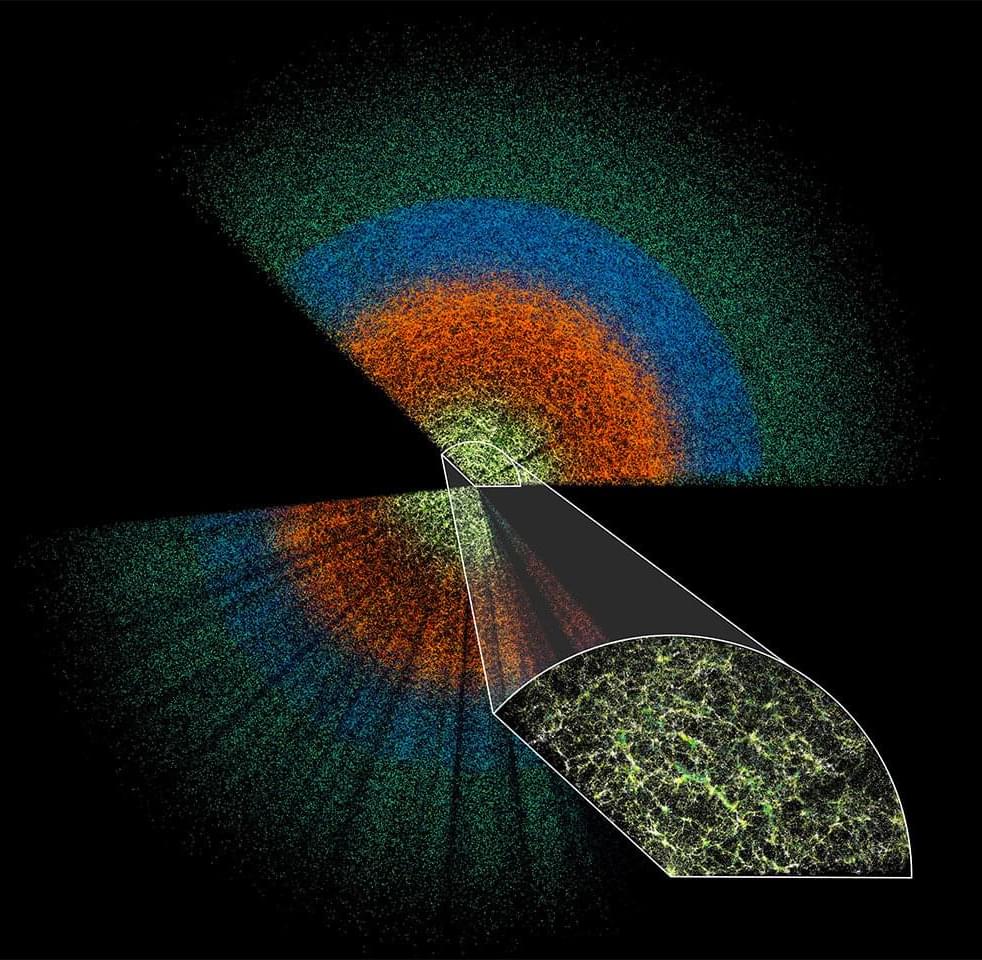
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is mapping millions of celestial objects to better understand dark energy—the mysterious driver of our universe’s accelerating expansion. Today, the DESI collaboration released a new collection of data for anyone in the world to investigate.
The dataset is the largest of its kind, with information on 18.7 million objects: roughly 4 million stars, 13.1 million galaxies, and 1.6 million quasars (extremely bright but distant objects powered by supermassive black holes at their cores).
While the experiment’s main mission is illuminating dark energy, DESI’s Data Release 1 (DR1) could yield discoveries in other areas of astrophysics, such as the evolution of galaxies and black holes, the nature of dark matter, and the structure of the Milky Way.