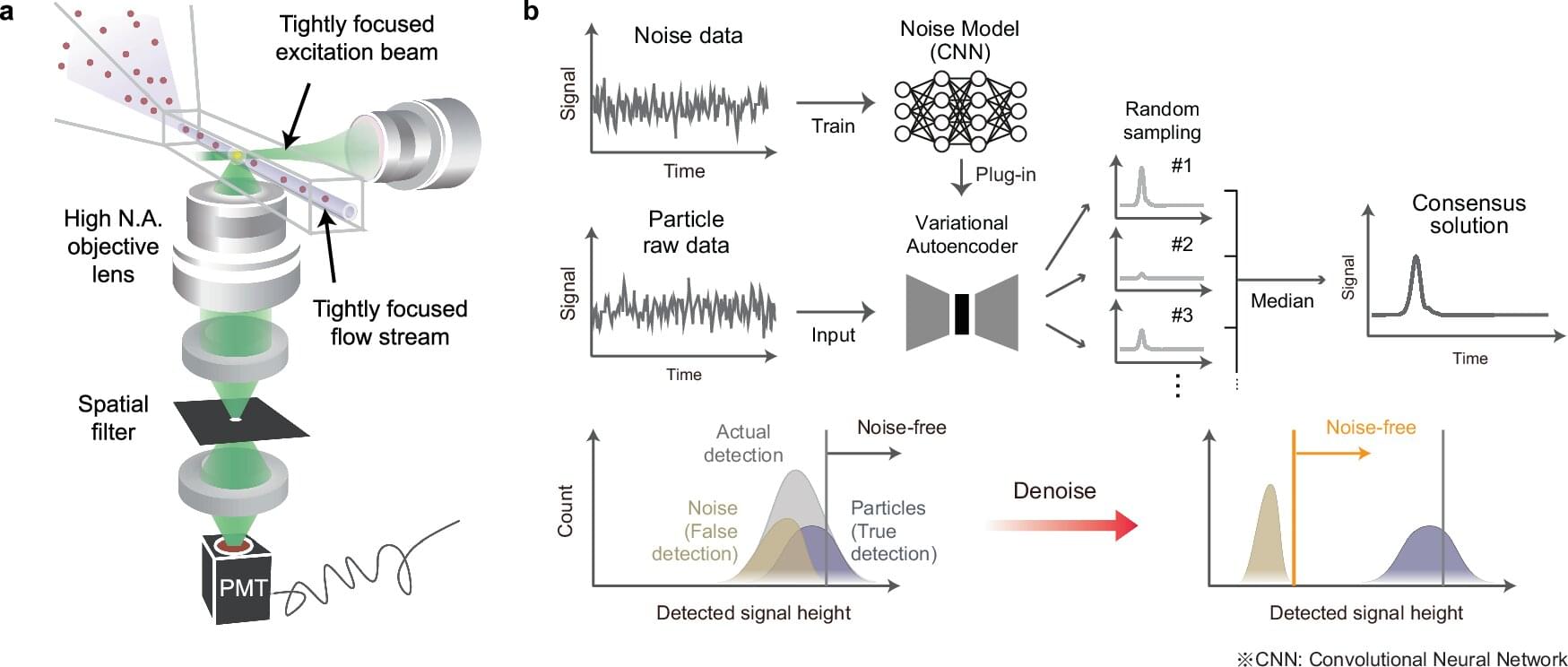
Researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, developed Deep Nanometry, an analytical technique combining advanced optical equipment with a noise removal algorithm based on unsupervised deep learning.
Deep Nanometry can analyze nanoparticles in medical samples at high speed, making it possible to accurately detect even trace amounts of rare particles. This has proven its potential for detecting extracellular vesicles indicating early signs of colon cancer, and it is hoped that it can be applied to other medical and industrial fields.
The body is full of microscopic particles smaller than cells. These include extracellular vesicles (EVs), which can be useful in early disease detection and also in drug delivery.