Antennas receive and transmit electromagnetic waves, delivering information to our radios, televisions, cellphones and more. Researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis imagines a future where antennas reshape even more applications.
Their new metasurfaces, ultra-thin materials made of tiny nanoantennas that can both amplify and control light in very precise ways, could replace conventional refractive surfaces from eyeglasses to smartphone lenses and improve dynamic applications such as augmented reality/virtual reality and LiDAR (light detection and ranging).
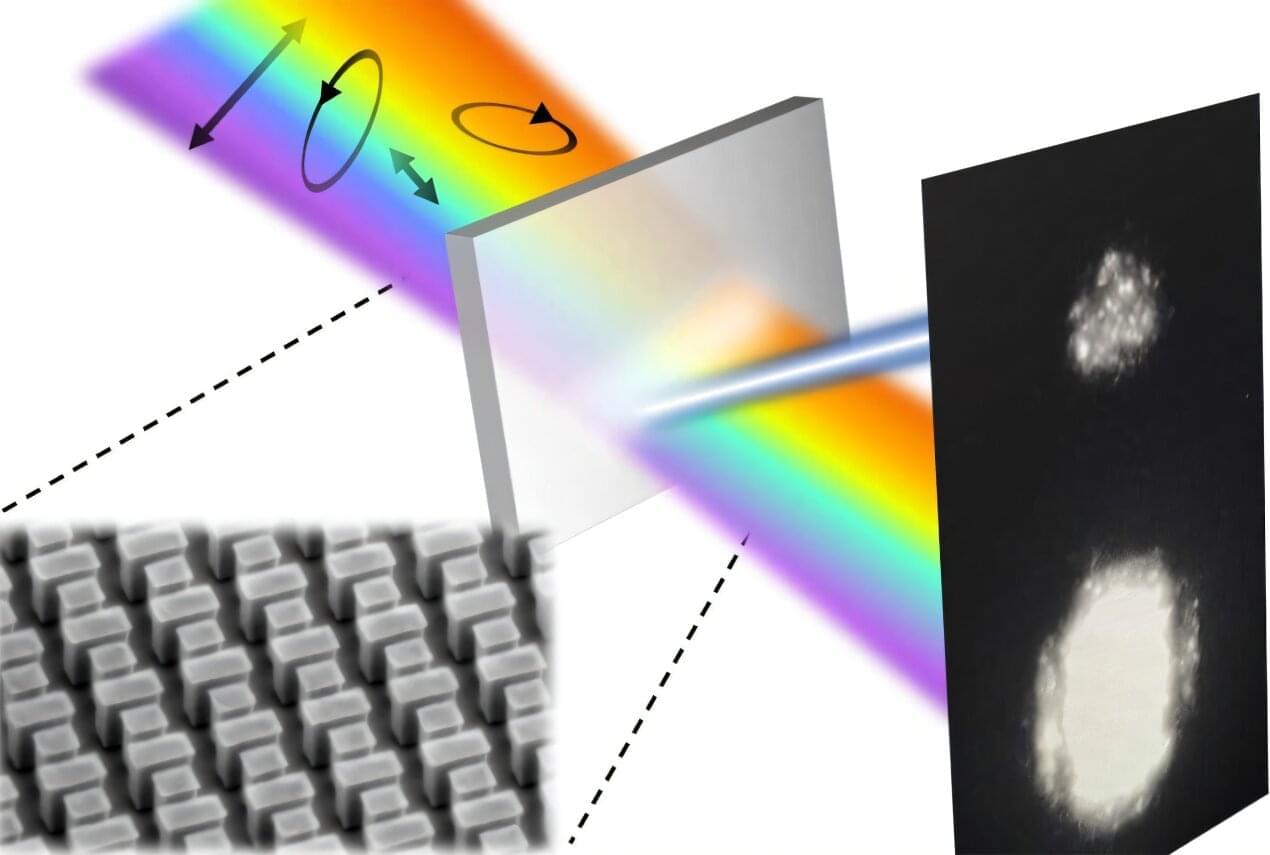
While metasurfaces can manipulate light very precisely and efficiently, enabling powerful optical devices, they often suffer from a major limitation: Metasurfaces are highly sensitive to the polarization of light, meaning they can only interact with light that is oriented and traveling in a certain direction. While this is useful in polarized sunglasses that block glare and in other communications and imaging technologies, requiring a specific polarization dramatically reduces the flexibility and applicability of metasurfaces.