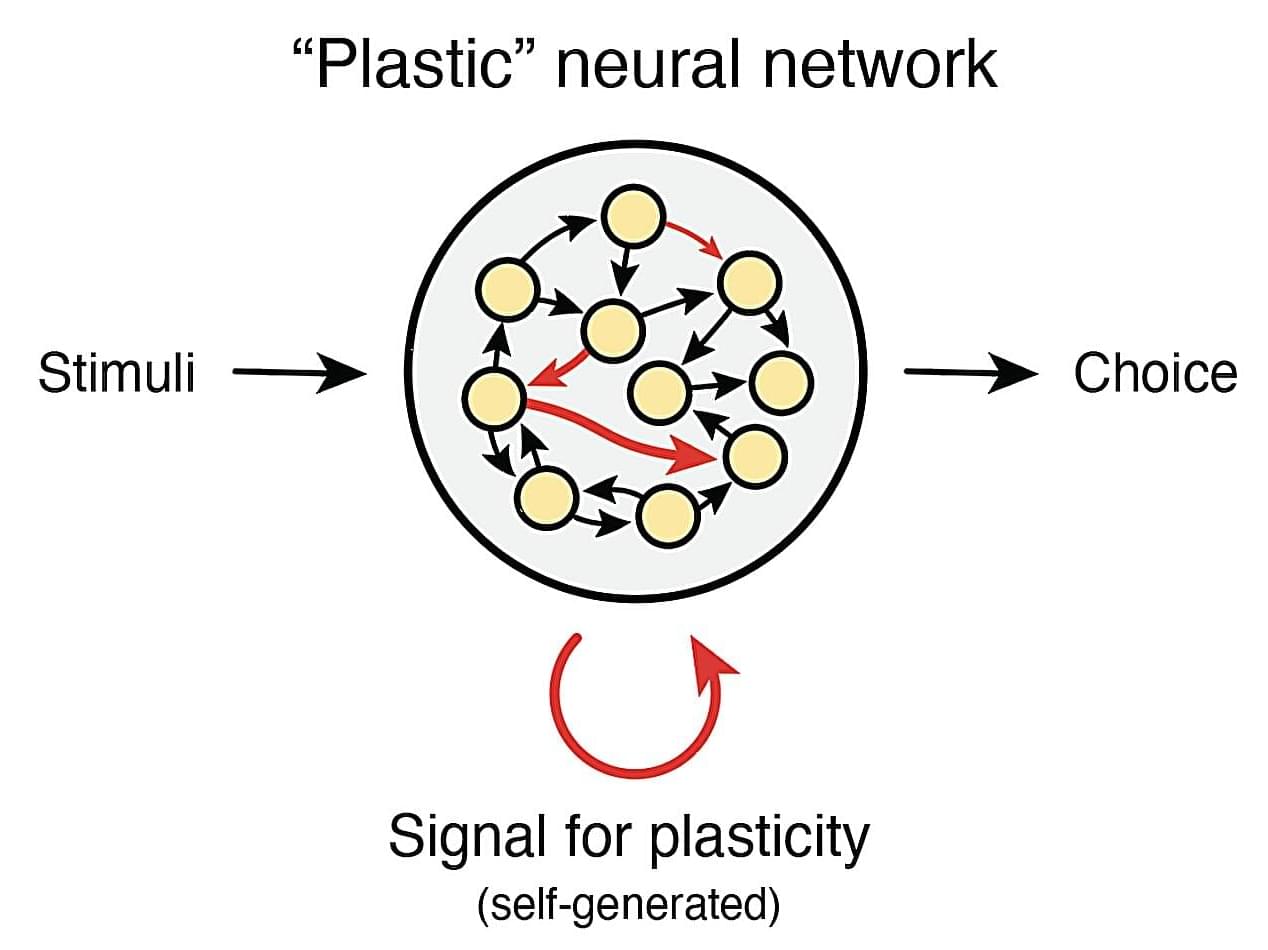
Humans and certain animals appear to have an innate capacity to learn relationships between different objects or events in the world. This ability, known as “relational learning,” is widely regarded as critical for cognition and intelligence, as learned relationships are thought to allow humans and animals to navigate new situations.
Researchers at ML Collective in San Francisco and Columbia University have conducted a study aimed at understanding the biological basis of relational learning by using a particular type of brain-inspired artificial neural network. Their work, published in Nature Neuroscience, sheds new light on the processes in the brain that could underpin relational learning in humans and other organisms.
“While I was visiting Columbia University, I met my co-author Kenneth Kay and we talked about his research,” Thomas Miconi, co-author of the paper, told Medical Xpress.