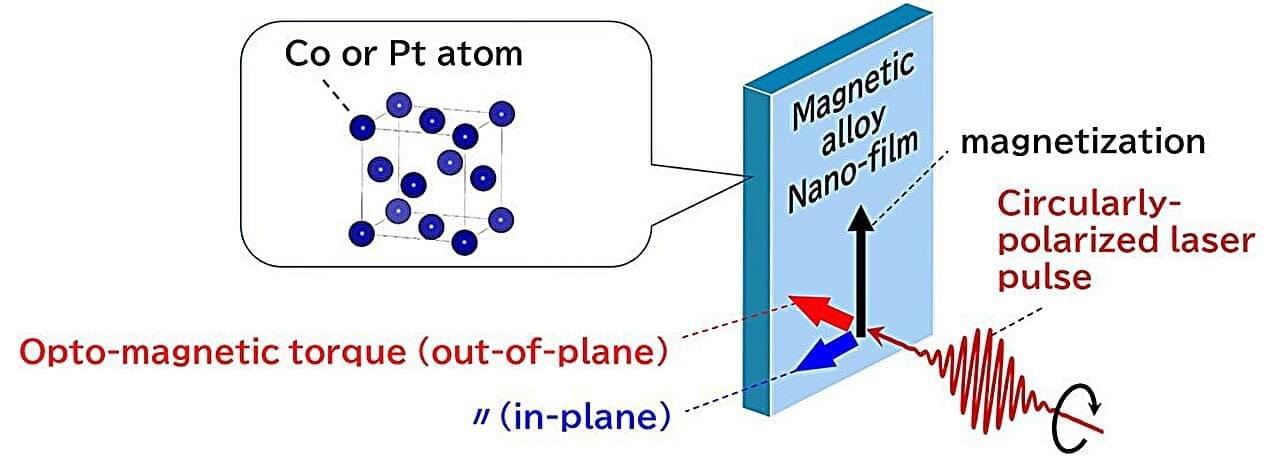
Researchers at Tohoku University have achieved a significant advancement in opto-magnetic technology, observing an opto-magnetic torque approximately five times more efficient than in conventional magnets. This breakthrough, led by Koki Nukui, Assistant Professor Satoshi Iihama, and Professor Shigemi Mizukami, has far-reaching implications for the development of light-based spin memory and storage technologies.
Opto-magnetic torque is a method which can generate force on magnets. This can be used to change the direction of magnets by light more efficiently. By creating alloy nanofilms with up to 70% platinum dissolved in cobalt, the team discovered that the unique relativistic quantum mechanical effects of platinum significantly boost the magnetic torque.
The study revealed that the enhancement of opto-magnetic torque was attributed to the electron orbital angular momentum generated by circularly polarized light and relativistic quantum mechanical effects. The findings are published in Physical Review Letters.