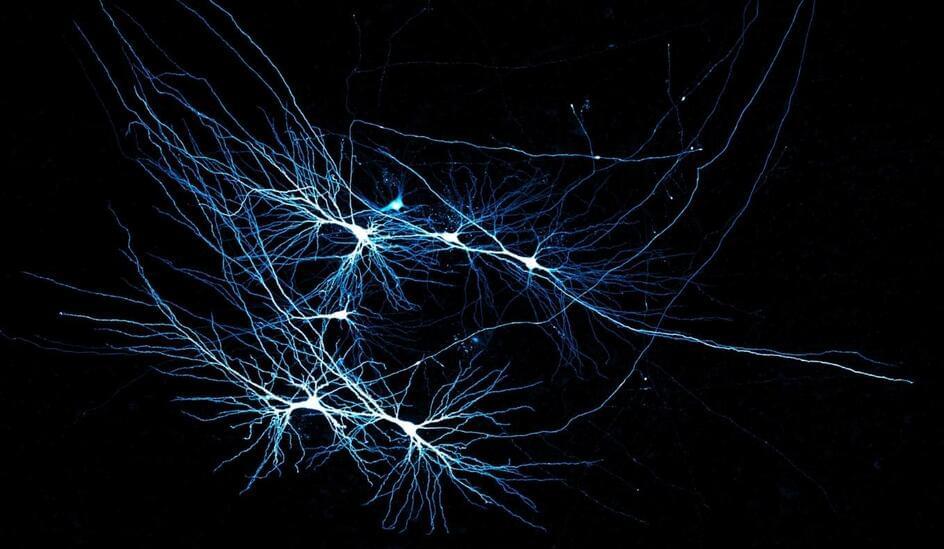
Our brain’s memory center bears a sleek design.
A peek into living tissue from human hippocampi, a brain region crucial for memory and learning, revealed relatively few cell-to-cell connections for the vast number of nerve cells. But signals sent via those sparse connections proved extremely reliable and precise, researchers report December 11 in Cell.
One seahorse-shaped hippocampus sits deep within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain. In each hippocampus’s CA3 area, humans have about 1.7 million nerve cells called pyramidal cells. This subregion is thought to be the most internally connected part of the brain in mammals.