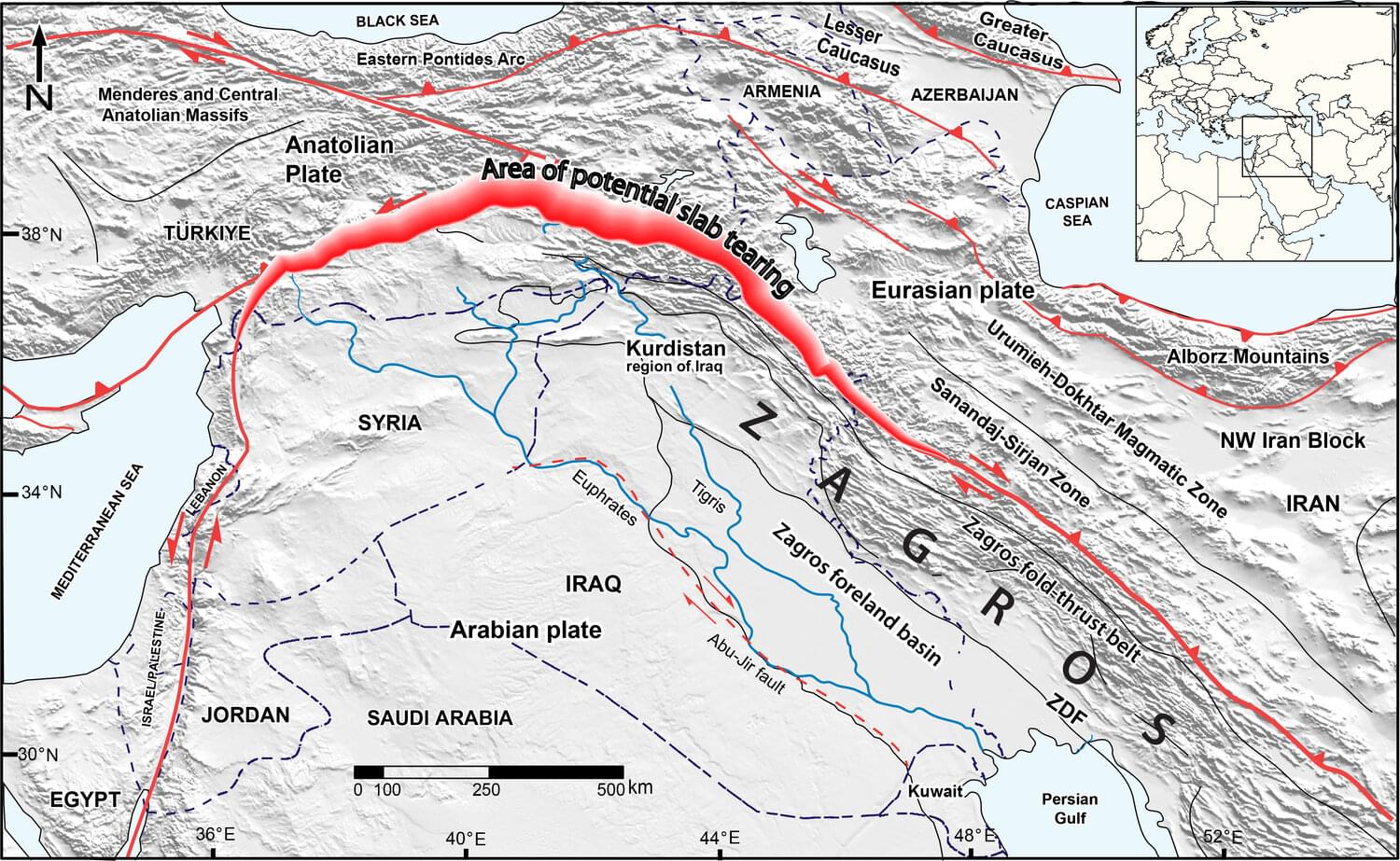
An international research team led by the University of Göttingen has investigated the influence of the forces exerted by the Zagros Mountains in the Kurdistan region of Iraq on how much the surface of the Earth has bent over the last 20 million years. Their research has revealed that in the present day, deep below the Earth’s surface, the Neotethys oceanic plate—the ocean floor that used to be between the Arabian and Eurasian continents—is breaking off horizontally, with a tear progressively lengthening from southeast Turkey to northwest Iran.
Their findings show how the evolution of the Earth’s surface is controlled by processes deep within the planet’s interior. The research is published in the journal Solid Earth.
When two continents converge over millions of years, the oceanic floor between them slides to great depths beneath the continents. Eventually, the continents collide, and masses of rock from their edges are lifted up into towering mountain ranges. Over millions of years, the immense weight of these mountains causes the Earth’s surface around them to bend downward. Over time, sediments eroded from the mountains accumulate in this depression, forming plains such as Mesopotamia in the Middle East.