To describe how matter works at infinitesimal scales, researchers designate collective behaviors with single concepts, like calling a group of birds flying in sync a “flock” or “murmuration.” Known as quasiparticles, the phenomena these concepts refer to could be the key to next-generation technologies.
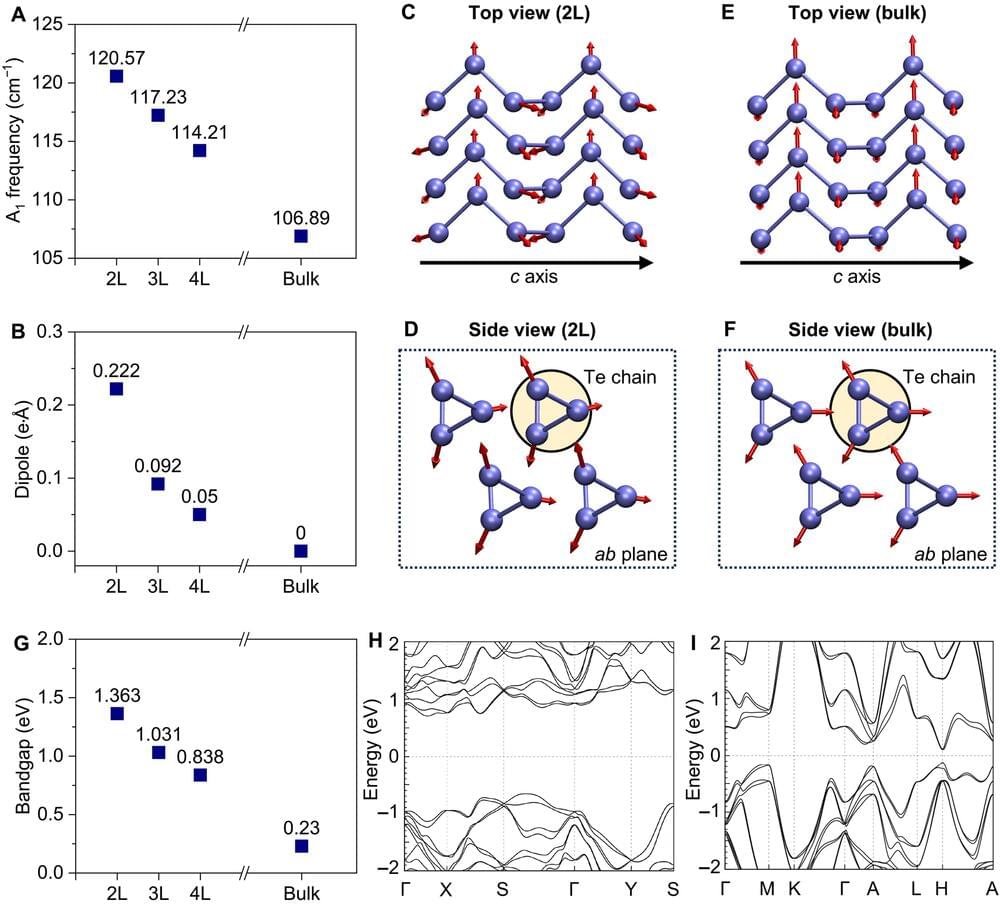
In a recent study published in Science Advances, a team of researchers led by Shengxi Huang, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering and materials science and nanoengineering at Rice, describe how one such type of quasiparticle—polarons—behaves in tellurene, a nanomaterial first synthesized in 2017 that is made up of tiny chains of tellurium atoms and has properties useful in sensing, electronic, optical and energy devices.
“Tellurene exhibits dramatic changes in its electronic and optical properties when its thickness is reduced to a few nanometers compared to its bulk form,” said Kunyan Zhang, a Rice doctoral alumna who is a first author on the study. “Specifically, these changes alter how electricity flows and how the material vibrates, which we traced back to the transformation of polarons as tellurene becomes thinner.”