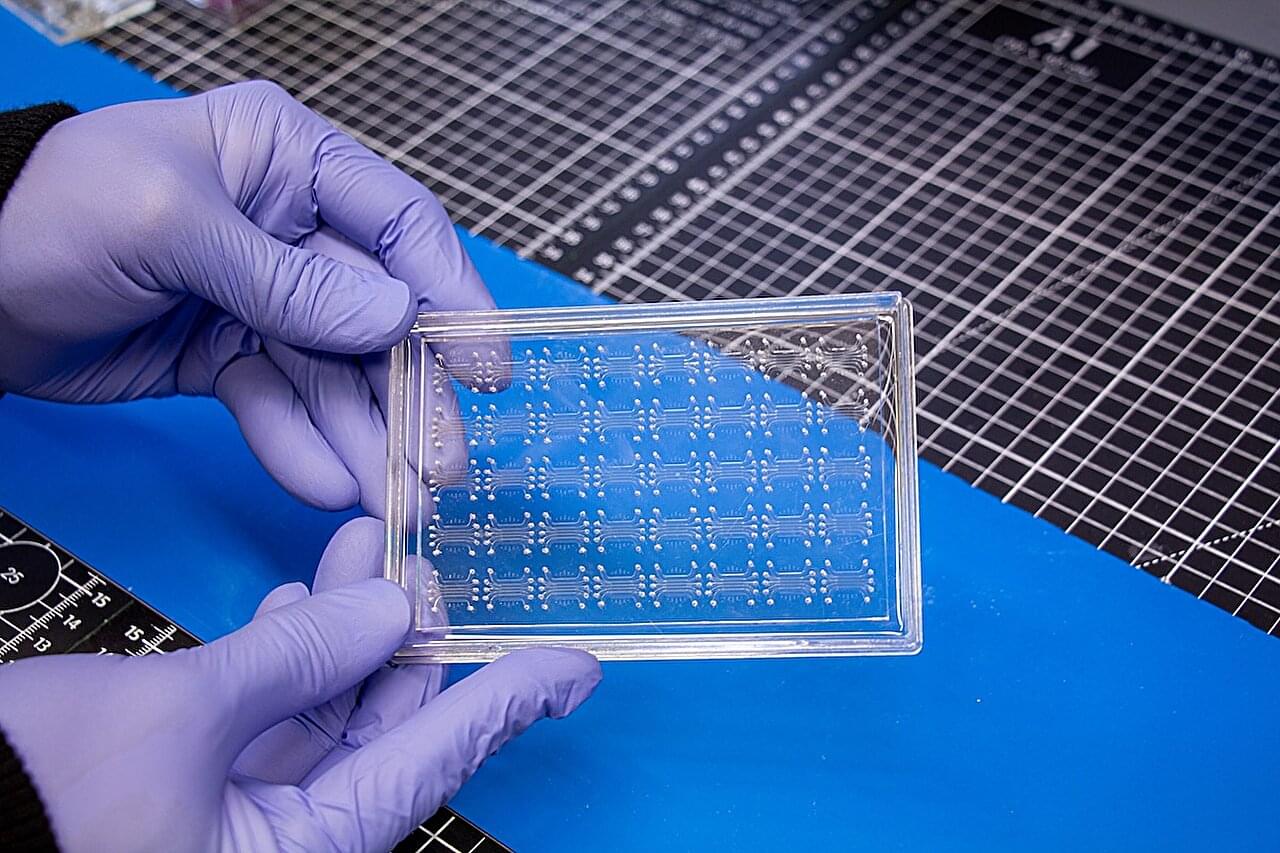
Hidden within our bones, marrow sustains life by producing billions of blood cells daily, from oxygen-carrying red cells to immune-boosting white cells. This vital function is often disrupted in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation, which can damage the marrow and lead to dangerously low white cell counts, leaving patients vulnerable to infection.
Now, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science (Penn Engineering), Perelman School of Medicine (PSOM) and the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a platform that emulates human marrow’s native environment. This breakthrough addresses a critical need in medical science, as animal studies often fail to fully replicate the complexities of human marrow.