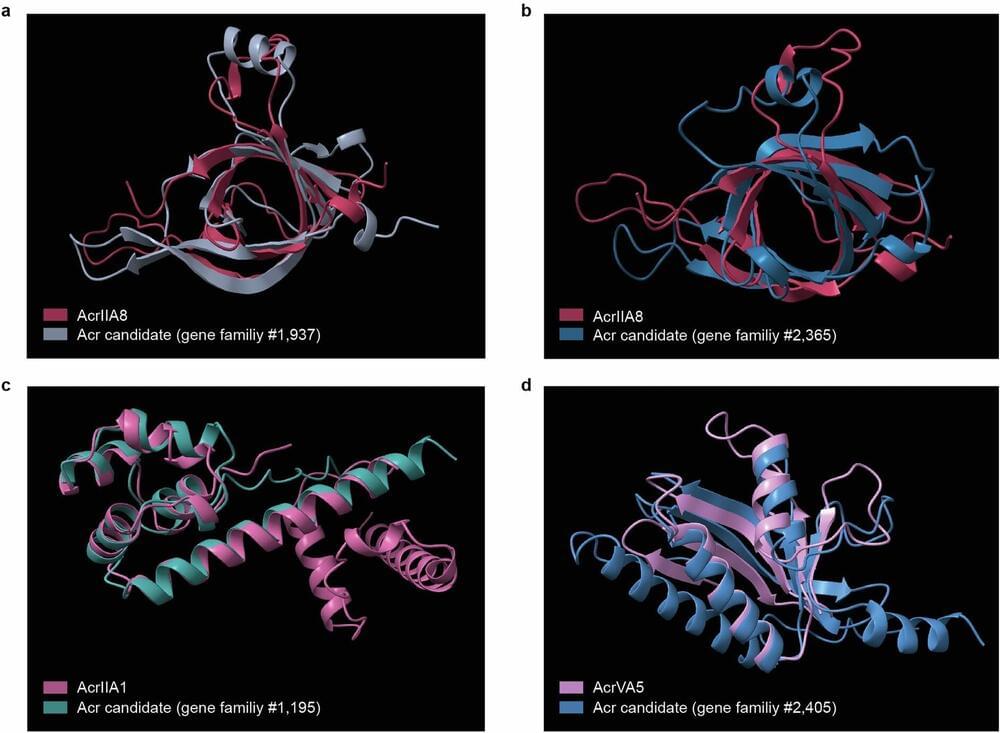
A new study by Tel Aviv University reveals how bacterial defense mechanisms can be neutralized, enabling the efficient transfer of genetic material between bacteria. The researchers believe this discovery could pave the way for developing tools to address the antibiotic resistance crisis and promote more effective genetic manipulation methods for medical, industrial, and environmental purposes.
The study was led by Ph.D. student Bruria Samuel from the lab of Prof. David Burstein at the Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research at Tel Aviv University’s Wise Faculty of Life Sciences. Other contributors to the research include Dr. Karin Mittelman, Shirly Croitoru, and Maya Ben-Haim from Prof. Burstein’s lab. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The researchers explain that genetic diversity is essential for the survival and adaptation of different species in response to environmental changes. For humans and many other organisms, sexual reproduction is the primary driver of the genetic diversity required for survival. However, bacteria and other microorganisms lack such a reproduction mechanism.