137 countries around the world have signed a “net-zero” climate change agreement to end fossil fuel use and achieve zero carbon emissions by 2050. Hydrogen is being touted as the next green energy source because it emits only water and oxygen when utilized as an energy source. Hydrogen production methods are divided into gray hydrogen, blue hydrogen, and green hydrogen depending on the energy source and carbon emissions. Among them, green hydrogen production method is the most eco-friendly method that produces hydrogen without carbon emissions by electrolyzing water using green energy.
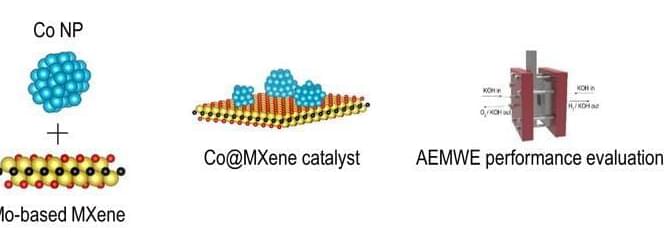
A research team led by Dr. Albert Sung Soo Lee of the Convergence Research Center for Solutions to Electromagnetic Interference in Future-Mobility and Materials Architecturing Research Center at Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) with collaboration with Professor Chong Min Koo’s group at Sungkyunkwan University has developed an oxidatively stable molybdenum-based MXene as electrocatalyst support in anion exchange membrane water electrolyzers. As it is stable against oxidative high voltage conditions, if it is applied as a carrier for electrolysis catalysts, it can be used as an oxygen evolution reaction electrode material for green hydrogen production to reduce the cost of green hydrogen production.
The research has been published in Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy (“Unveiling the role of catalytically active MXene supports in enhancing the performance and durability of cobalt oxygen evolution reaction catalysts for anion exchange membrane water electrolyzers”).