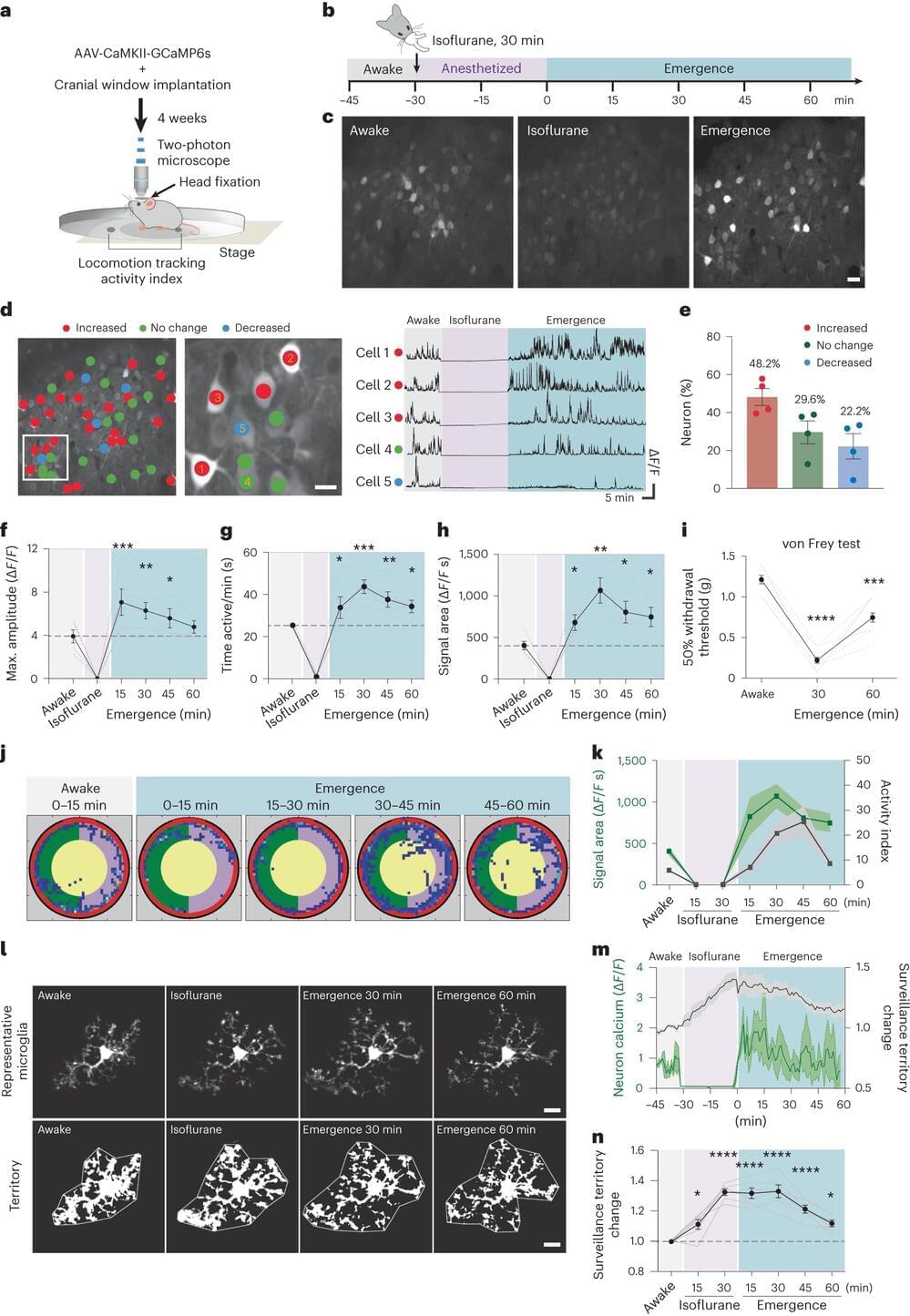
According to a Mayo Clinic study published in Nature Neuroscience, the cells that act as the central nervous system’s first line of defense against harm also play a role in helping the brain awaken from anesthesia. This discovery could help pave the way for innovative methods that address post-anesthesia complications.
When coming out of anesthesia, more than one-third of patients can experience either extreme drowsiness or hyperactivity, a side effect called delirium. Mayo researchers found that special immune cells in the brain called microglia can act to shield neurons from the aftereffects of anesthesia to awaken the brain.
“This is the first time we’ve seen microglia enhance and boost neuronal activity by physically engaging the brain circuits,” says Mayo Clinic neuroscientist Long-Jun Wu, senior author of the study.